SQL面试题
语法基础
CURD
1 | INSERT INTO TABLE (XXX)VALUE( XX,XX) |
查询
DISTINCT(去重)
1 | SELECT DISTINCT name, city FROM users; |
LIMIT()
限制返回的行数。第一个参数为起始行,从 0 开始;第二个参数为返回的总行数
1 | //返回前5行 |
排序
- ASC:升序
- DESC:降序
可以按多个列进行排序,并且为每个列指定不同的排序方式:
1 | SELECT * |
过滤
| 操作符 | 示例 SQL | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
= |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE city = '北京'; |
等于 |
< |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE age < 20; |
小于 |
> |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE score > 90; |
大于 |
<> 或 != |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE city <> '北京'; |
不等于 |
<= / !> |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE age <= 18; |
小于等于 |
>= / !< |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE score >= 90; |
大于等于 |
BETWEEN |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE score BETWEEN 80 AND 90; |
在两值之间(包含边界) |
IS NULL |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE remark IS NULL; |
是 NULL |
IS NOT NULL |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE remark IS NOT NULL; |
不是 NULL |
AND |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE age > 18 AND score > 80; |
同时满足两个条件 |
OR |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE city = '北京' OR city = '上海'; |
满足任一条件 |
() 优先级 |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE city='北京' OR (age < 20 AND score > 80); |
加括号调整逻辑 |
IN |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE city IN ('北京', '上海'); |
等价于多个 OR |
IN (SELECT ...) |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE id IN (SELECT id FROM scores WHERE score>90); |
从子查询匹配 |
NOT |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE NOT city = '北京'; |
否定条件 |
通配符
| 通配符 | 示例 SQL | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
%(>=0 个字符) |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE name LIKE '张%'; |
匹配所有以“张”开头的名字,例如“张三”、“张小明” |
%abc% |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE city LIKE '%京%'; |
匹配包含“京” 的城市,例如“北京”、“南京” |
_(=1 个字符) |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE name LIKE '_三'; |
匹配第二个字是“三”的两个字名字,如“张三”,但不匹配“王小三” |
[ab] |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE name LIKE '[李王]%'; (部分数据库支持,如 SQL Server) |
匹配姓李或姓王的学生 |
[^ab] |
SELECT * FROM students WHERE name LIKE '[^李王]%'; |
匹配不姓李也不姓王的学生 |
计算字段
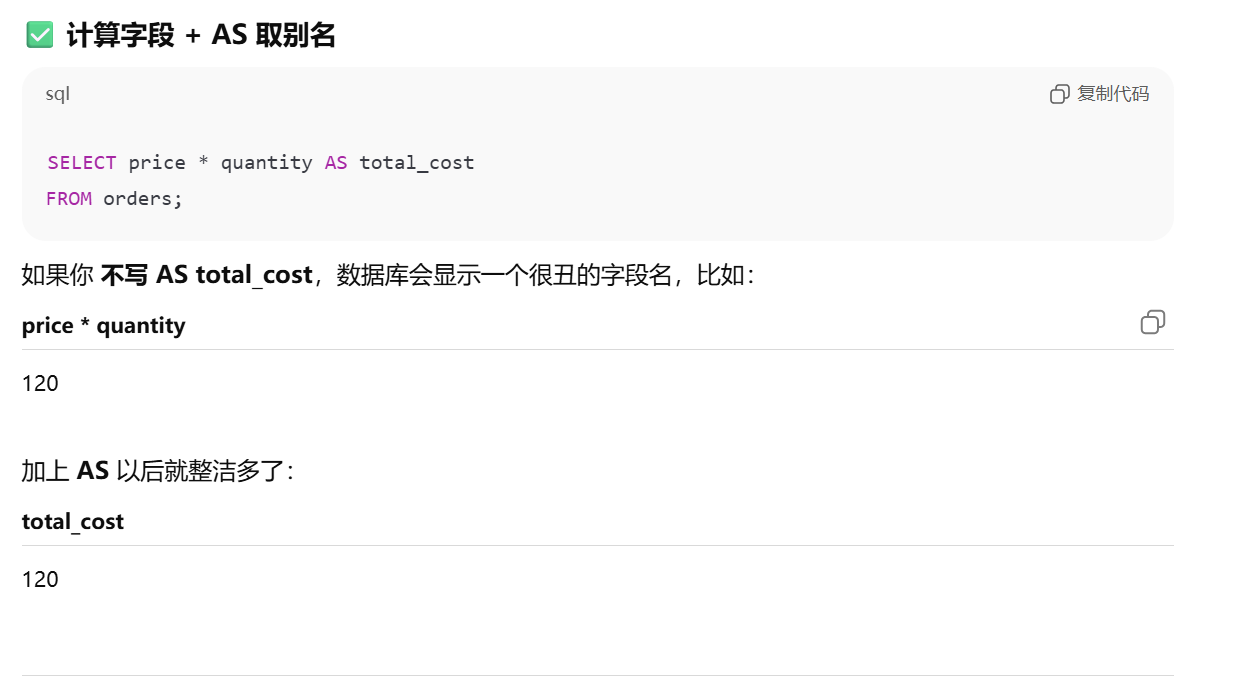
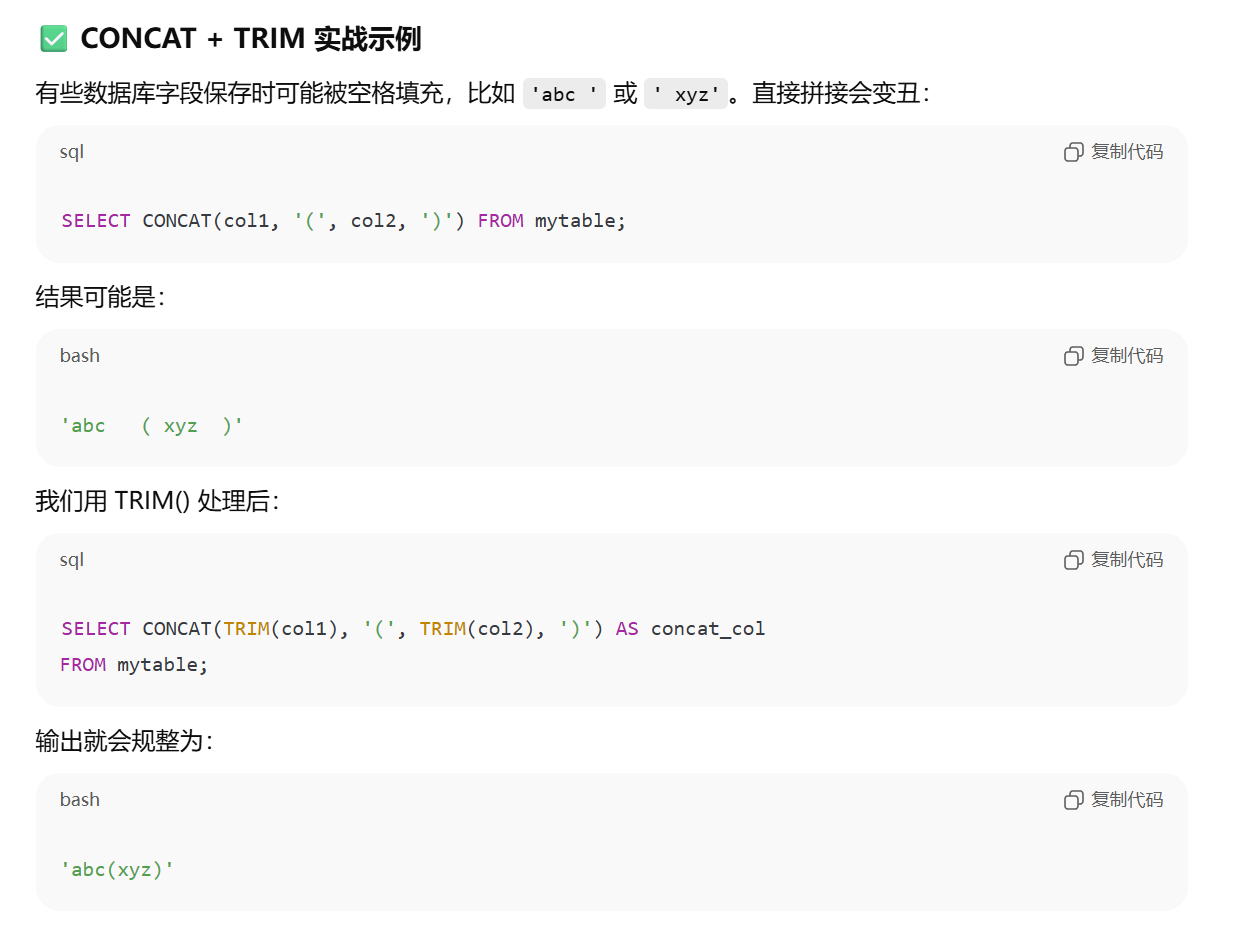
函数
汇总(重要)
| 汇总函数 | 作用 | 示例 SQL | 示例结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
COUNT(*) |
计算总行数(包含 NULL) | SELECT COUNT(*) FROM students; |
5 |
COUNT(col) |
统计非 NULL 的个数 | SELECT COUNT(score) FROM students; |
4(NULL 被忽略) |
AVG(col) |
计算平均值(忽略 NULL) | SELECT AVG(score) FROM students; |
(85+90+75+95) / 4 = 86.25 |
SUM(col) |
求和(忽略 NULL) | SELECT SUM(score) FROM students; |
85+90+75+95 = 345 |
MAX(col) |
最大值 | SELECT MAX(score) FROM students; |
95 |
MIN(col) |
最小值 | SELECT MIN(score) FROM students; |
75 |
1 | AVG |
 、
、
1 | ACG( DISTINCT col) 只会对不同的col做汇总 |
日期&文本
数组处理
分组!(重要)
分组 其实就是把相同的数据值的行放到同一组中
通过我们会要求 返回的是每一组的一个汇总情况
指定的分组字段除了能按该字段进行分组,也会自动按该字段进行排序。即group by会自动排序
WHERE 过滤行,HAVING 过滤分组,行过滤应当先于分组过滤。
1 | SELECT cal,SUM(age) AS cnt FROM TABLE |

规则
- 除了那个汇总字段外,select里出现的字段都应该在 group by中给出
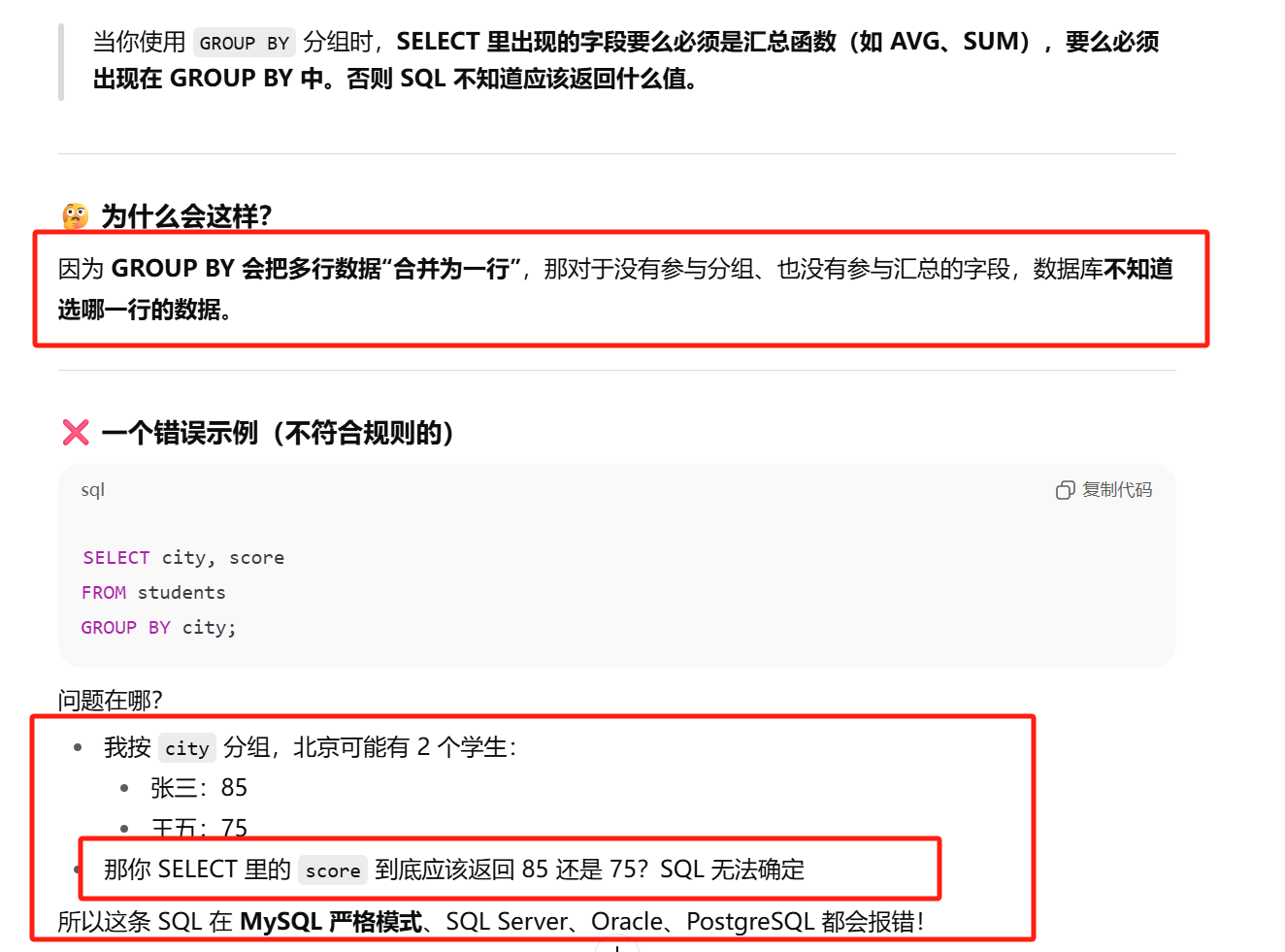
- order by 应该在 group by之后

- NULL 的行会单独分为一组;
- MySQL 的group by不支持blog text,其实大多数 SQL 实现不支持 GROUP BY 列具有可变长度的数据类型。PS:char()为固定,varchar()为可变

子查询
!!!子查询只能返回一个字段的数据
可以将子查询的结果作为 WHRER 语句的过滤条件:
1 | SELECT * |
下面的语句可以检索出客户的订单数量,子查询语句会对第一个查询检索出的每个客户执行一次:
1 | SELECT cust_name, (SELECT COUNT(*) |
标量子查询
1️⃣ 结构分析
- 外层 SELECT
1 | SELECT (子查询) AS SecondHighestSalary |
- 外层 SELECT 里只有一个表达式:一个 标量子查询
- 标量子查询(scalar subquery)返回 单个值
- 即使没有匹配的行,MySQL 也会返回一行,值为
NULL
- 子查询
1 | SELECT salary FROM Rank_S WHERE sRank = 2 LIMIT 1 |
- 查找
sRank = 2的工资 - 如果存在多行(同一工资多个员工),
LIMIT 1保证只取 一行 - 如果不存在第二高工资(比如表里只有一条记录),子查询 不返回任何行 → 标量子查询自动返回 NULL
2️⃣ 为什么保证一行输出
- 外层 SELECT 不依赖表,只是用标量子查询生成一列
- MySQL 规则:
标量子查询如果没有返回值 → 结果为 NULL
- 外层 SELECT 至少会输出一行(列名 SecondHighestSalary,值为 NULL 或工资值)
3️⃣ 对比普通子查询
1 | SELECT salary FROM Rank_S WHERE sRank = 2; |
- 直接查询,没找到行 → 返回 0 行
- 不是标量子查询,外层没有包裹 → 可能没有任何结果行
4️⃣ 总结
- 标量子查询 + 外层 SELECT → 总是返回一行
- LIMIT 1 保证即使有多行,也只取一行
- 没有匹配值 → 返回 NULL
- ✅ 这就是为什么你写法“即使没有第二名,也会返回一行结果”
连接
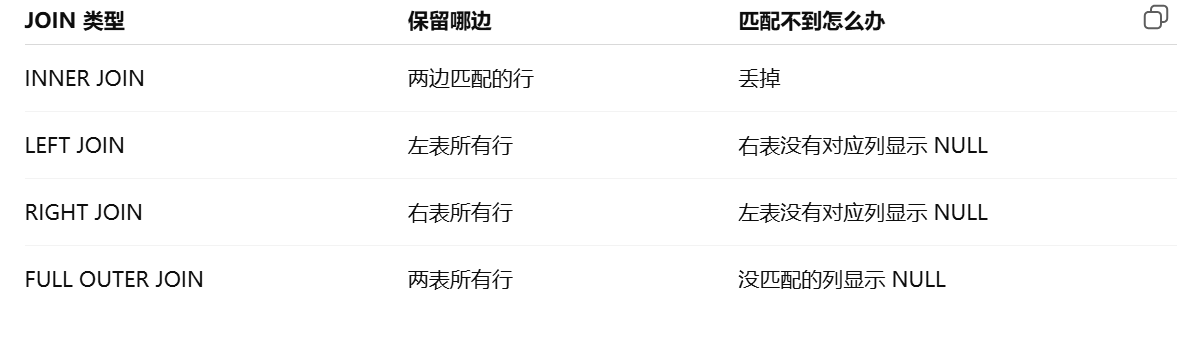
连接用于连接多个表,使用 JOIN 关键字,并且条件语句使用 ON 而不是 WHERE。
连接可以替换子查询,并且比子查询的效率一般会更快。
可以用 AS 给列名、计算字段和表名取别名,给表名取别名是为了简化 SQL 语句以及连接相同表
其实就是根据某个条件把两张表的数据给拼接到一起
内连接
eg:
1 | SELECT A.value AS A_value, B.value AS B_value |
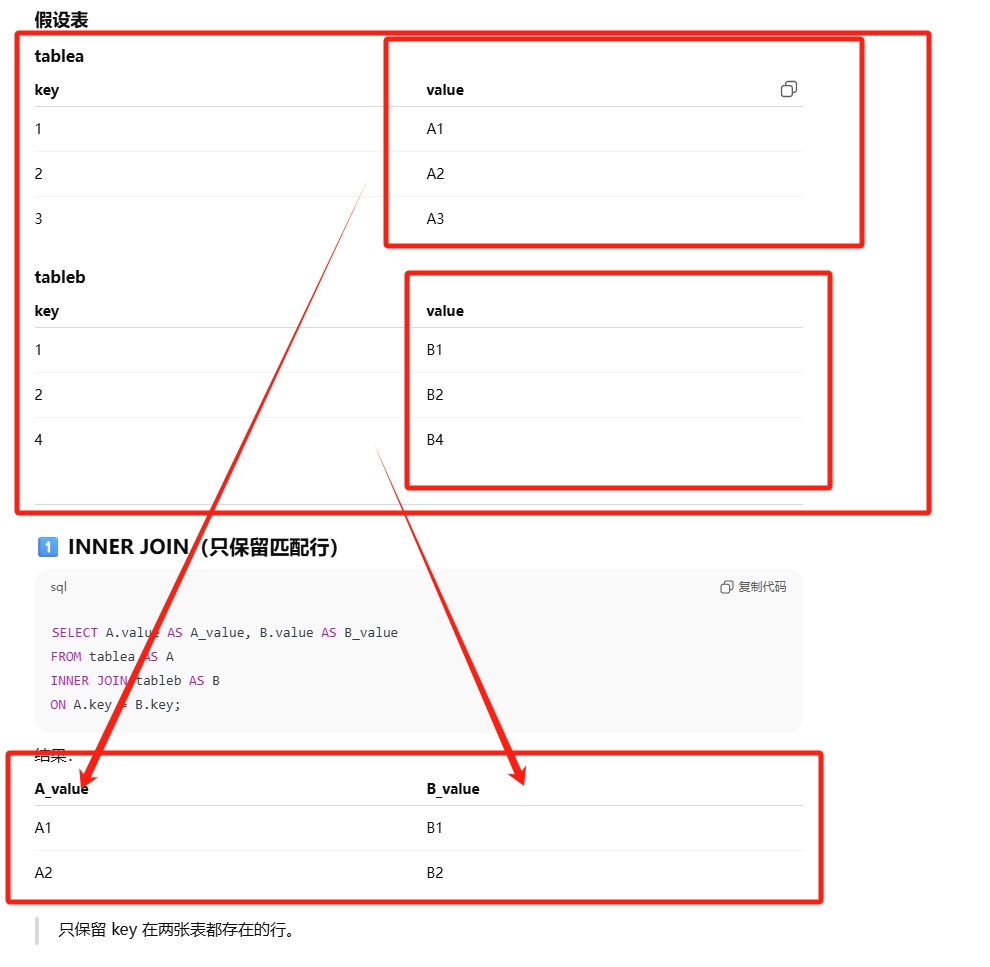
可以不明确使用 INNER JOIN,而使用普通查询并在 WHERE 中将两个表中要连接的列用等值方法连接起来。
1 | SELECT A.value, B.value |
在没有条件语句的情况下返回笛卡尔积
PS:内连接;在没有条件语句的情况下返回笛卡尔积。
自连接
自连接可以看成内连接的一种,只是连接的表是自身而已。
一张员工表,包含员工姓名和员工所属部门,要找出与 Jim 处在同一部门的所有员工姓名。
子查询版本
1 | SELECT name |
自连接版本
1 | SELECT e1.name |
1 | ON e1.department = e2.department |
解释:
e1.department = e2.department:找和某人同部门的员工
e2.name = “Jim”:指定 e2 这一行是 “Jim”
换句话说,就是:查找和 Jim 在同一个部门的所有员工。
外连接
外连接保留了没有关联的那些行。分为左外连接,右外连接以及全外连接,左外连接就是保留左表没有关联的行。
检索所有顾客的订单信息,包括还没有订单信息的顾客。
1 | SELECT Customers.cust_id, Orders.order_num |
customers 表:
| cust_id | cust_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | a |
| 2 | b |
| 3 | c |
orders 表:
| order_id | cust_id |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 3 |
结果:
| cust_id | cust_name | order_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a | 1 |
| 1 | a | 2 |
| 3 | c | 3 |
| 3 | c | 4 |
| 2 | b | Null |
组合查询
使用 UNION 来组合两个查询,如果第一个查询返回 M 行,第二个查询返回 N 行,那么组合查询的结果一般为 M+N 行。
每个查询必须包含相同的列、表达式和聚集函数。
默认会去除相同行,如果需要保留相同行,使用 UNION ALL。
只能包含一个 ORDER BY 子句,并且必须位于语句的最后。
总结:
- 合并两个或多个 SELECT 查询的结果
- 默认会 去掉重复行
- 如果想保留重复行,用
UNION ALL - 要求:
- 每个查询的列数必须相同
- 对应列的数据类型要兼容
- ORDER BY 只能在最后使用一次
可以理解为把查询结果 “上下拼接在一起”
1 | SELECT col |
MYSQL 8 窗口函数(重要)
窗口函数(Window Function)是 SQL 中用于在不分组的前提下对行进行计算的强大功能,尤其适用于排名、累计求和、移动平均等场景。
常用窗口函数
| 分类 | 函数 | 常见用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 累计/聚合 | SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX(), MIN() |
累计和 / 移动平均 |
| 排序 / 排名 | ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), DENSE_RANK() |
Top N、去重排序 |
| 偏移比较 | LAG(), LEAD() |
比较当前行与上一/下一行 |
| 统计总数 | NTILE() |
分组分位(如四分位) |
窗口函数细则
| 分类 | 函数 | 典型语法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 累计 / 聚合 | SUM(expr) |
SUM(weight) OVER (ORDER BY turn) |
累积求和 |
AVG(expr) |
AVG(score) OVER (PARTITION BY class) |
组内平均 | |
COUNT(expr) |
COUNT(*) OVER (ORDER BY date) |
累计计数 | |
MAX(expr) |
MAX(salary) OVER (PARTITION BY dept) |
每组最大值 | |
MIN(expr) |
MIN(salary) OVER () |
全局最小值 | |
| 排序 / 排名 | ROW_NUMBER() |
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY dept ORDER BY salary DESC) |
连续排名(无并列) |
RANK() |
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY score DESC) |
有并列,跳号 | |
DENSE_RANK() |
DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY score DESC) |
有并列,不跳号 | |
| 偏移比较 | LAG(expr, offset, default) |
LAG(salary, 1, 0) OVER (ORDER BY id) |
取上一行数据 |
LEAD(expr, offset, default) |
LEAD(salary) OVER (ORDER BY id) |
取下一行数据 | |
| 分布统计 | NTILE(n) |
NTILE(4) OVER (ORDER BY score DESC) |
分成 4 份(四分位) |
PERCENT_RANK() |
PERCENT_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY score) |
百分比排名 | |
CUME_DIST() |
CUME_DIST() OVER (ORDER BY score) |
累计分布比例 | |
| 位置 / 首尾 | FIRST_VALUE(expr) |
FIRST_VALUE(salary) OVER (PARTITION BY dept ORDER BY salary) |
组内第一个 |
LAST_VALUE(expr) |
LAST_VALUE(salary) OVER (...) |
默认要配 frame 子句 | |
NTH_VALUE(expr, n) |
NTH_VALUE(score, 2) OVER (...) |
取第 n 个 |
OVER语法
OVER,OVER 里只能出现 PARTITION BY 和 ORDER BY
| 写法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
OVER() |
不分组也不排序,整个表算 |
OVER(PARTITION BY ...) |
在每个组内计算 |
OVER(ORDER BY ...) |
按顺序逐行累积 |
OVER(PARTITION BY ... ORDER BY ...) |
分组后再排序计算 |
大厂真题
百度
2021年11月每天的人均浏览文章时长_牛客题霸_牛客网
统计2021年11月每天的人均浏览文章时长(秒数),结果保留1位小数,并按时长由短到长排序
分析:
:::info
sum(out_time - in_time) / count(distinct uid) as avg_time where 月份 group by day order by avg_time
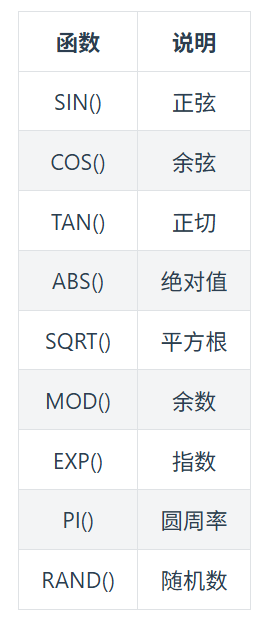
函数使用:
人均:sum(out_time - in_time) / count(distinct uid)
每天的:group by day
2021年11月:where date_time() = “”
保留1位小数:Round( value,1)
:::
1 |