排序
排序数组[321]
思路
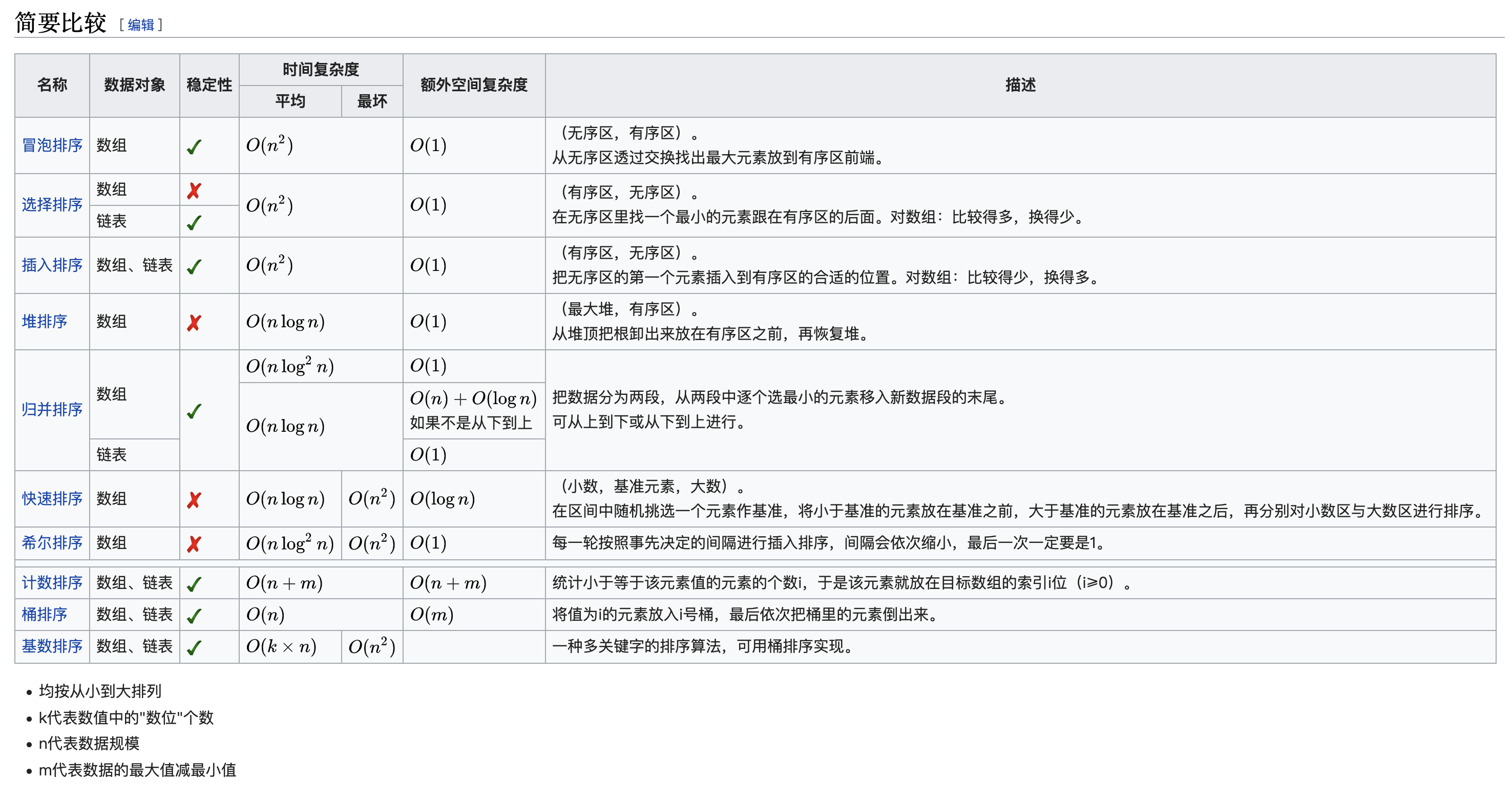
快排,堆,计数,归并
- 快排
1 | class Solution { |
- 题目特殊性,时间复杂度为O(N)的解法,采用计数排序
1 |
|
- 归并排序
1 | class Solution { |
字典序排数[13]
思路:
1 | class Solution { |
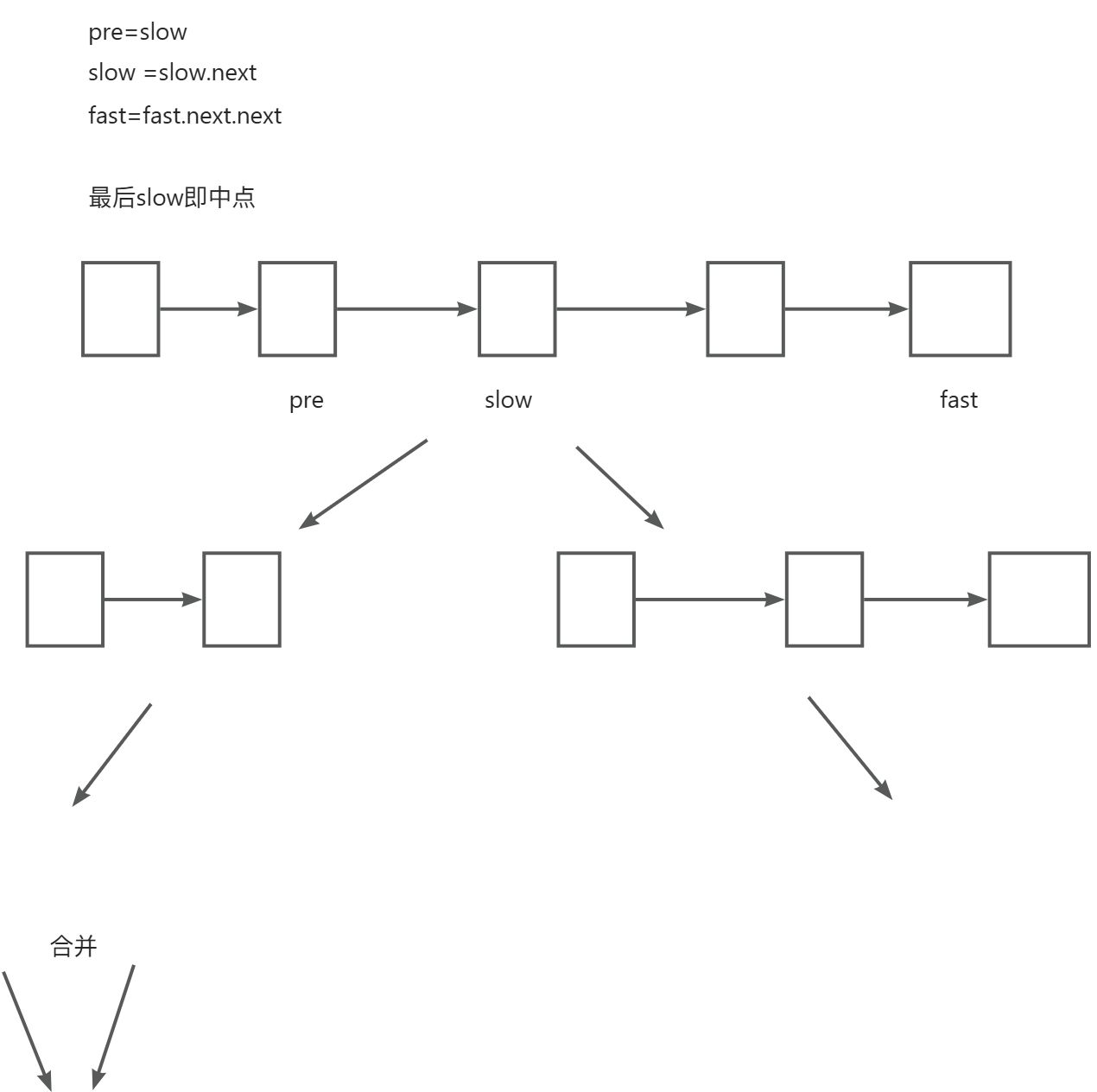
排序链表[133]
思路:
- 归并排序
head….tail-> head….mid mid…tail
不断分,然后并起来
归:对链表进行分割,直到每个链表只有一个 元素
并:对链表进行升序合并
链表取中点(快慢指针),并切割
- 快排(容易超时)
图(归并)
1 | /** |
时间复杂度:NlogN 空间复杂度:logN
合并K个排序链表[221]
思路:
- 归并排序
- 堆(可能需要手写)排序
1 | /** |
- 时间复杂度:O(Llogm),其中 m 为 lists 的长度,L 为所有链表的长度之和。
数组中的第K个最大元素[550]
题目:
- 要求时间复杂度为O(N)
思路:
- 维护size == k的最小堆(但不符合题意)时间复杂度:nums.length log(k)
1 | class Solution { |
- 快速选择
思路:
- 构建partition函数,里面干的就是 数组随机取一个 x,然后划分
x - 如何划分!?
1、小技巧,先将 l 和 x交换,方便后面处理
2、curL–> …. <—curR,while把curL和curR推进到需要交换的位置,然后swap,交换后,重复这个过程
外层while(true) 内层while 推进curL,curR。若curR<=curL退出全部循环
3、将x放回正确位置,—> swap(l,curR)
- 经过划分我们可以得到
x。那么这个时候判断x的index 和 targetIndex( n - k)的位置 - 若 index = targertIdex 就是找到答案了,直接返回。若index > targetIndex 则说明targetIndex在右边,那么这个时候让r = index缩小范围,反之,让l = index
1 | class Solution { |
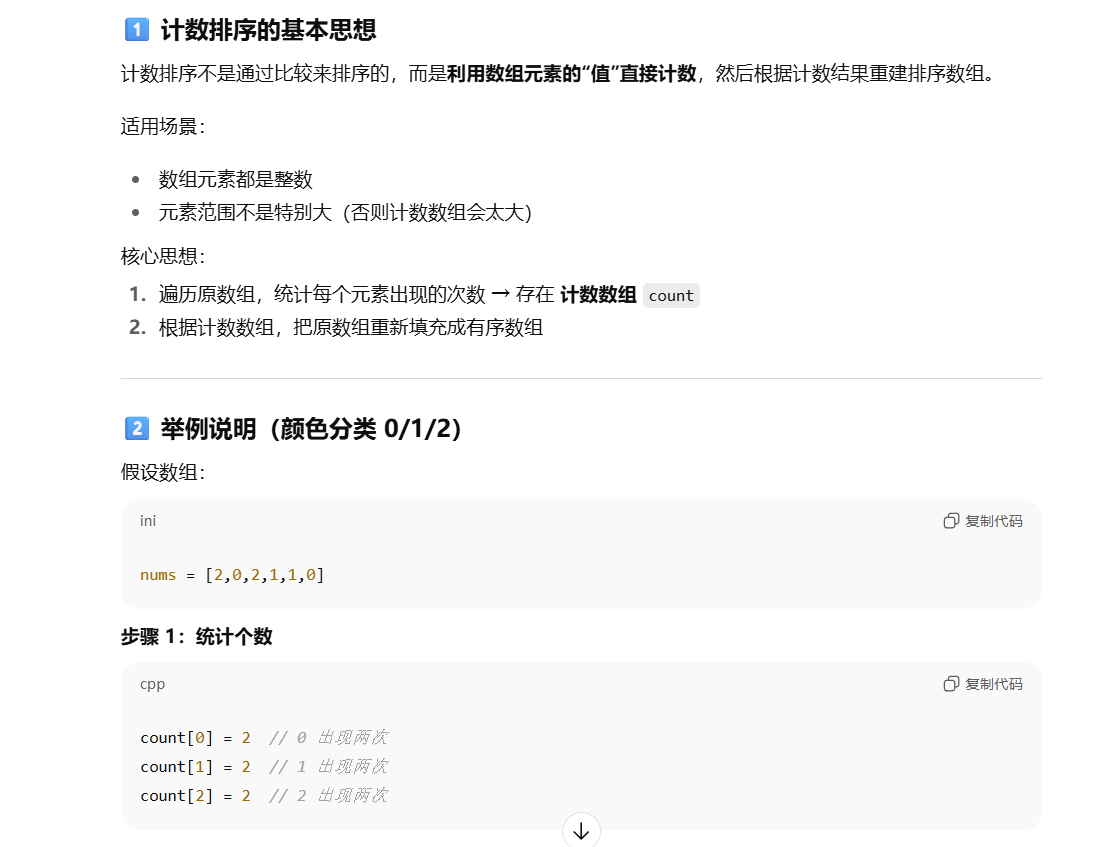
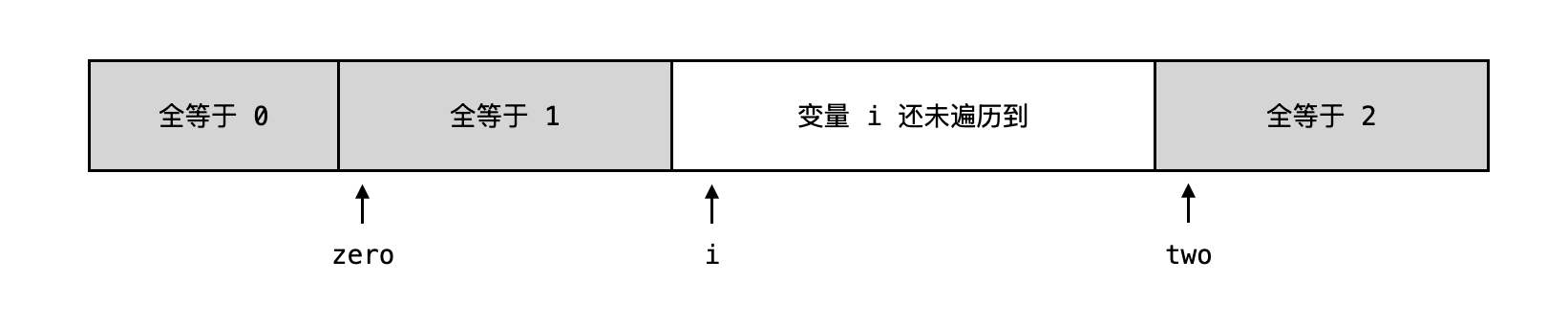
颜色分类[41]
思路:
- 三路快排(三指针法)。0…zero i two…n -1
1 |
|
或者计数排序
1 | class Solution { |