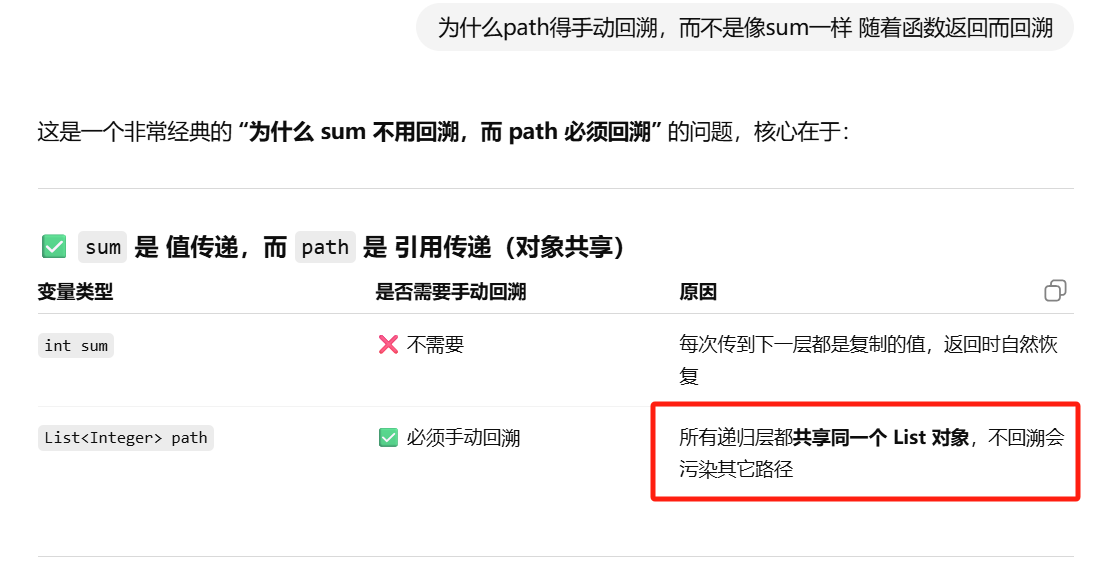
必看
回溯模版的解释
思路:
1.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class Solution {
int [][]direct={{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}};
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
res++;
dfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(char [][]grid,int x,int y){
if(x<0||y<0||x>=grid.length||y>=grid[0].length){
return;
}
if(grid[x][y]=='0'){
return;
}
else {
grid[x][y]='0';
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nextX=x+direct[i][0];
int nextY=y+direct[i][1];
dfs(grid,nextX,nextY);
}
}
}
|
@週刊少年 时间复杂度BFS会低一点,空间复杂度感觉DFS会好一点(但是要考虑递归调用的堆栈的空间就不好说了)
被问到深度优先和广度优先的差别、计算时间空间复杂度
面试用BFS写出来了,然后让我用并查集再写一个,字节
思路:
- used[i] 用于控制 防止走回头路
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path=new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
boolean []used=new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(nums,used);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int []nums,boolean []used){
if(path.size()==nums.length){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(used[i]){
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
used[i]=true;
dfs(nums,used);
path.removeLast();
used[i]=false;
}
}
}
|
时间复杂度:
| 问题类型 |
是否需要 startIndex |
控制逻辑 |
示例 |
| 排列 Permutation |
❌ 不需要 |
用 used[i] 防止重复选 |
[1,2] vs [2,1] 都算不同 |
| 组合 Combination |
✅ 必须 |
用 startIndex 防止重复,为了防止来回选,必须 保证后面的选择只能从当前元素后面开始。 |
[1,2] 和 [2,1] 视为相同 |
去重版的全排列 I,用HashSet存结果集即可
思路:
- spring
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| class Solution {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
Set<Integer> wait = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> completed = new HashSet<>();
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++) graph.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
for(int[] pre : prerequisites) graph.get(pre[1]).add(pre[0]);
for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++)
if(!completed.contains(i) && !dfs(i)) return false;
return true;
}
private boolean dfs(int course) {
if(wait.contains(course)) return false;
if(completed.contains(course)) return true;
wait.add(course);
for(int next : graph.get(course)) {
if(!dfs(next)) return false;
}
wait.remove(course);
completed.add(course);
return true;
}
}
|
思路:
DFS + 记忆化搜索
还是得把回溯树给画出来,才清晰易懂!!!(明天来搞)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-break/solutions/302779/shou-hui-tu-jie-san-chong-fang-fa-dfs-bfs-dong-tai/
竟然可以记忆化,说明可以转成DP
判断可能性大概率是 DP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
Boolean []memory ;
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
memory = new Boolean[s.length()];
return dfs(s, 0, wordDict);
}
public boolean dfs(String s,int startIndex,List<String> wordDict){
if(startIndex == s.length()) return true;
if(memory[startIndex] != null){
return memory[startIndex];
}
for(String word: wordDict){
int nextStartIndex = startIndex + word.length();
if(nextStartIndex > s.length()){
continue;
}
if(s.startsWith(word, startIndex) && dfs(s,nextStartIndex,wordDict)){
memory[startIndex] = true;
return true;
}
}
memory[startIndex] = false;
return false;
}
}
|
思路:
- 回溯,最基础的题了。可以细想一下这个递归,最容易的一次
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| [abc]
[iop]
交叉相乘,笛卡尔集
排列何尝不是一种算 笛卡尔集合
[a b c]
[a b c]
[a b c]
abb 只不过递归的集合不断为自己本身
for (int i = 0; i < t.get(tIndex).length(); i++) {
path.append(t.get(tIndex).charAt(i));
dfs(tIndex + 1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| class Solution {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap();
List<String> t = new ArrayList();
List<String> res = new ArrayList();
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
map.put(1, "");
map.put(2, "abc");
map.put(3, "def");
map.put(4, "ghi");
map.put(5, "jkl");
map.put(6, "mno");
map.put(7, "pqrs");
map.put(8, "tuv");
map.put(9, "wxyz");
for (char c : digits.toCharArray()) {
t.add(map.get(c - '0'));
}
dfs(0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int tIndex) {
if (path.length() == t.size()) {
res.add(path.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t.get(tIndex).length(); i++) {
path.append(t.get(tIndex).charAt(i));
dfs(tIndex + 1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
}
}
}
|
思路
- 将左右括号 -+化
- 对于path,则在参数中update

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| class Solution {
Set<String> res = new HashSet();
int max = 0;
String s;
int n;
int maxPathLen = 0;
public List<String> removeInvalidParentheses(String _s) {
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
s = _s;
n = s.length();
for(char c: s.toCharArray()){
if(c == '(') l++;
else if(c == ')') r++;
}
max = Math.max(l, r);
dfs(0, "", 0);
return new ArrayList(res);
}
public void dfs(int curCharIndex, String path, int score){
if(score < 0 || score > max) return;
if(curCharIndex == n){
if(score == 0 && path.length() >= maxPathLen){
if(path.length() > maxPathLen) res.clear();
maxPathLen = path.length();
res.add(path);
}
return;
}
char c = s.charAt(curCharIndex);
if(c == '('){
dfs(curCharIndex + 1, path + c, score + 1);
dfs(curCharIndex + 1, path, score);
}
else if(c == ')'){
dfs(curCharIndex + 1, path + c, score - 1);
dfs(curCharIndex + 1, path, score);
}
else dfs(curCharIndex + 1, path + c, score);
}
}
|
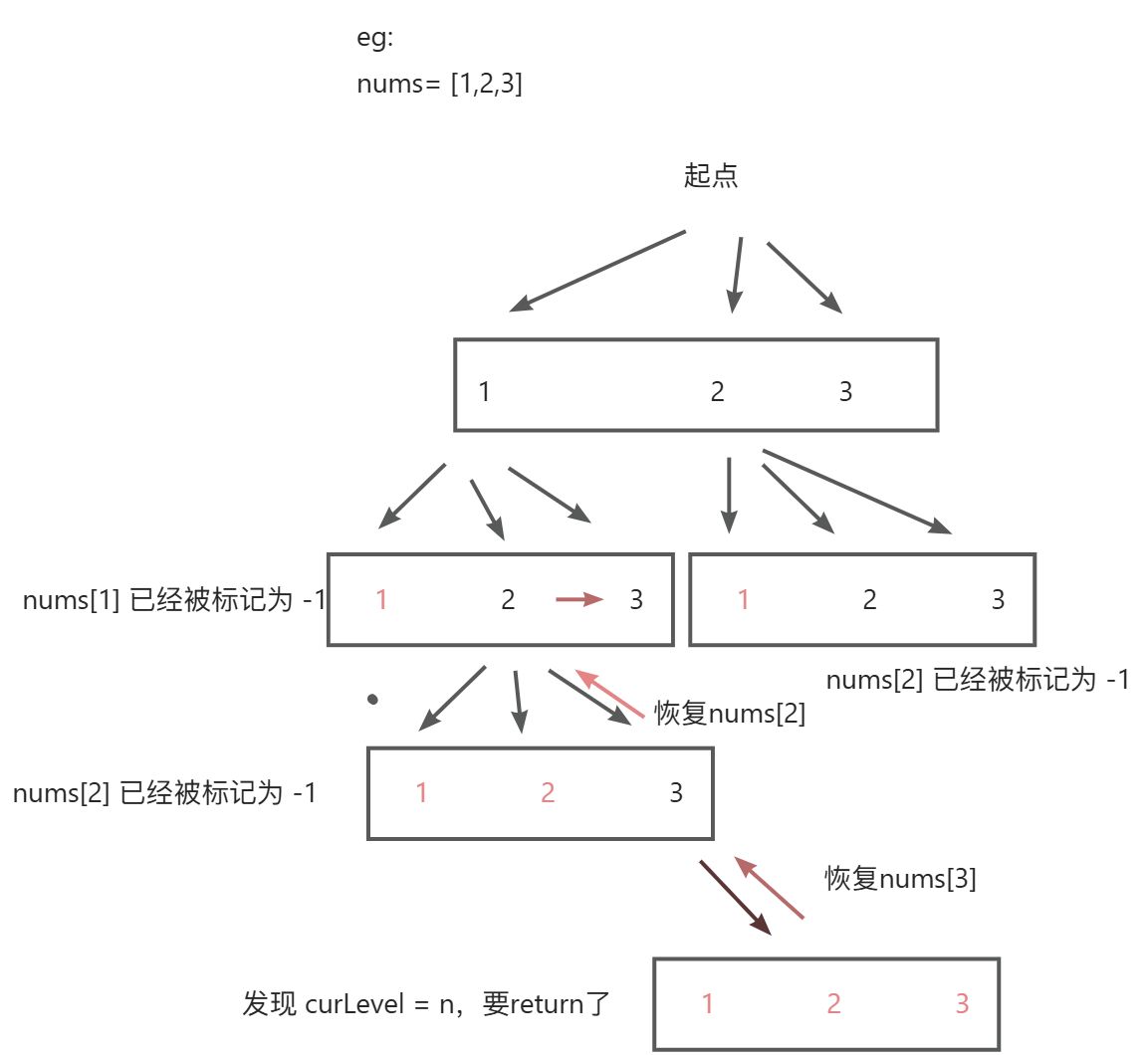
戳气球
思路
- dfs + 回溯,有一个n层的数组,然后我往下走,戳当前i节点,并在下次递归之前把当前节点置为 -1,防止重复选,curLevel == n时更新结果。但超时,得进行记忆化
回溯树:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| class Solution {
int n;
int res = 0;
public int maxCoins(int[] nums) {
n = nums.length;
dfs(nums, 0, 0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, int curLevel, int curCoin){
if(curLevel == n){
res = Math.max(res, curCoin);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] == -1){
continue;
}
int midQ = nums[i];
int lQ = 1;
int rQ = 1;
int l = i - 1;
int r = i + 1;
while(l >= 0 && nums[l] == -1){
l--;
}
if(l < 0) lQ = 1;
else lQ = nums[l];
while(r < nums.length && nums[r] == -1){
r++;
}
if(r >= nums.length) rQ = 1;
else rQ = nums[r];
int add = lQ * midQ * rQ;
nums[i] = -1;
dfs(nums, curLevel + 1, curCoin + add);
nums[i] = midQ;
}
}
}
|
时间复杂度 = O(n! × n)
- dp,dp[i][j] 表示 i 到 j能获得的最大金币
- dp[i][j] = 区间内的最大。那么dp[i][i + len] = res;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
public int maxCoins(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] temp = new int[n+2];
temp[0] = 1;
temp[n+1] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
temp[i+1] = nums[i];
}
int[][] dp = new int[n+2][n+2];
for(int len=3; len<=n+2; len++){
for(int i=0; i<=n+2-len; i++){
int res = 0;
for(int k = i+1; k<i+len-1; k++){
int left = dp[i][k];
int right = dp[k][i+len-1];
res = Math.max(res, left + temp[i]*temp[k]*temp[i+len-1] + right);
}
dp[i][i+len-1] = res;
}
}
return dp[0][n+1];
}
}
|
思路
- DFS
- 每个节点两种选择 + or -
比较简单的回溯,和普通的回溯的区别,就是在循环过程中,如果是像组合排列这些题,就需要往后遍历找,即树的宽度不定,而这题则树宽为 1,每次直接一个数递归下去即可,不用循环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
dfs(nums, target, 0, 0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int numIndex, int sum){
if(numIndex == nums.length){
if(target == sum) res++;
return ;
}
dfs(nums, target, numIndex + 1, sum + nums[numIndex]);
dfs(nums, target, numIndex + 1, sum - nums[numIndex]);
}
}
|

题目:
求叶子节点到根节点 路径和 为target的路径
思路:
- dfs 回溯。
- 注意!!! 叶子结点定义,root.left == null && root.right == null
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return new ArrayList(res);
dfs(root, targetSum, 0, new ArrayList());
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum, int sum, List<Integer> path) {
if (root == null) {
return ;
}
sum += root.val;
path.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
if (sum == targetSum)
res.add(new ArrayList(path));
}
dfs(root.left, targetSum, sum, path);
dfs(root.right, targetSum, sum, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
|