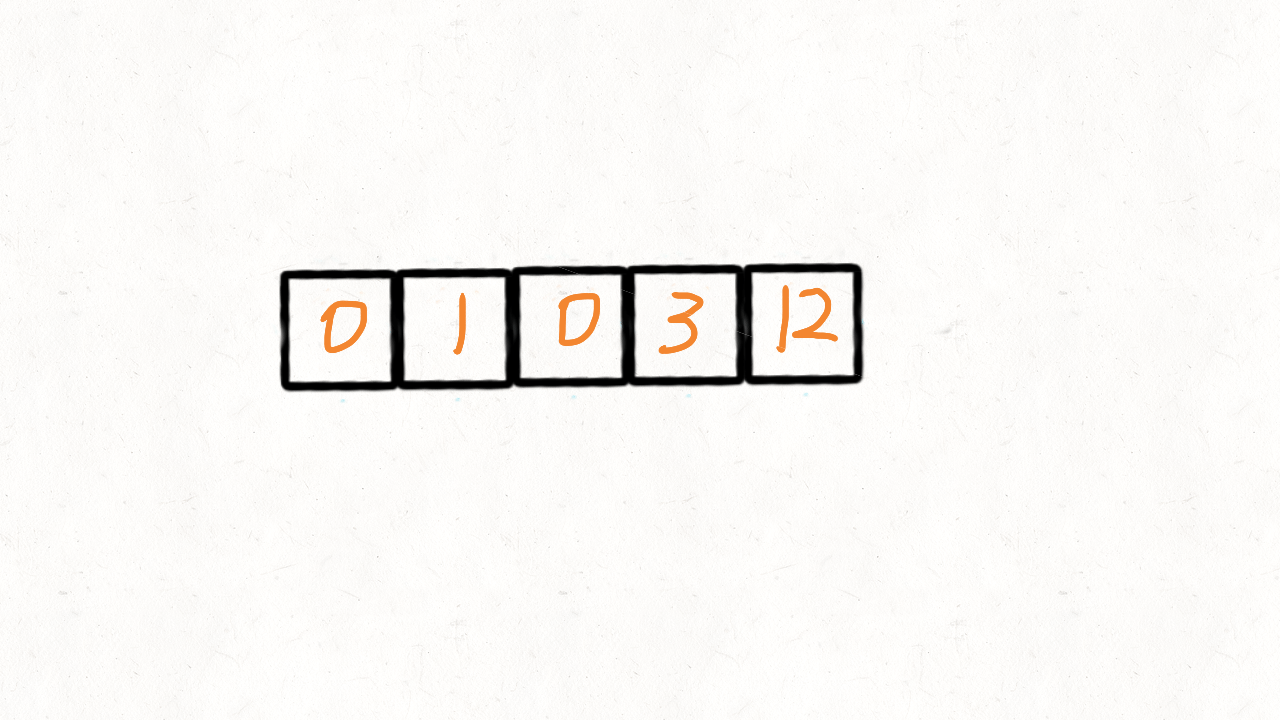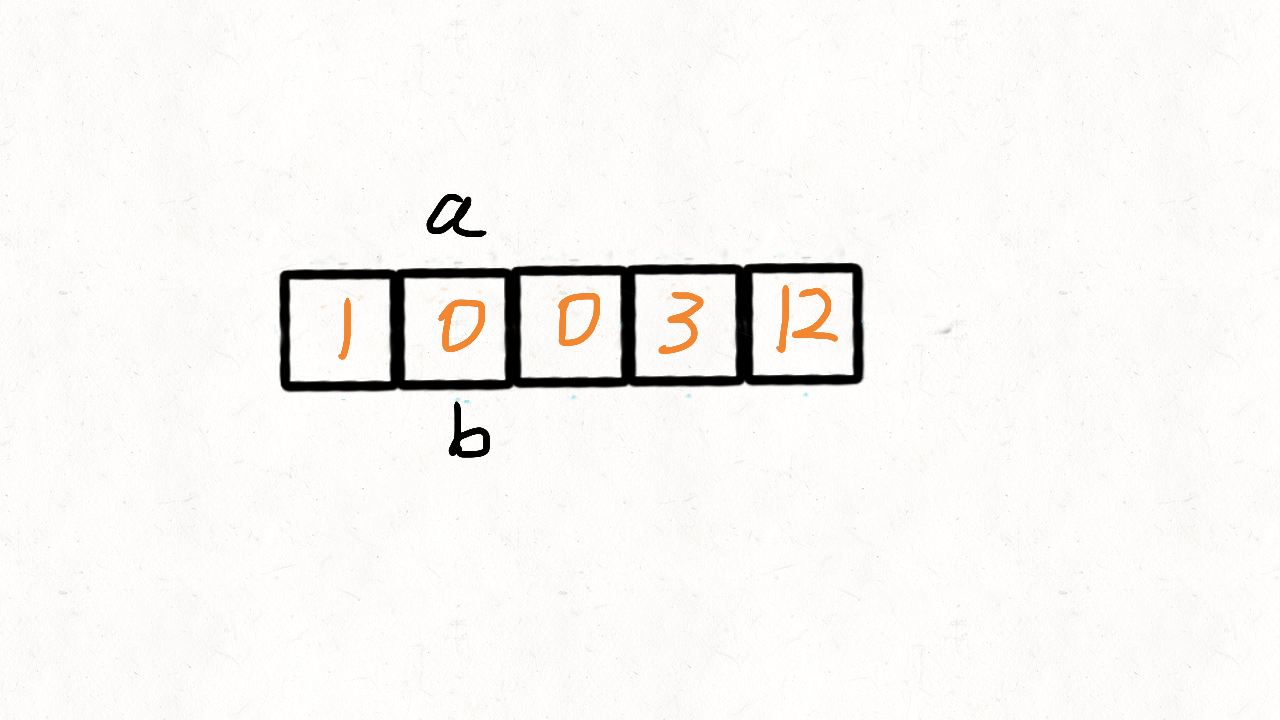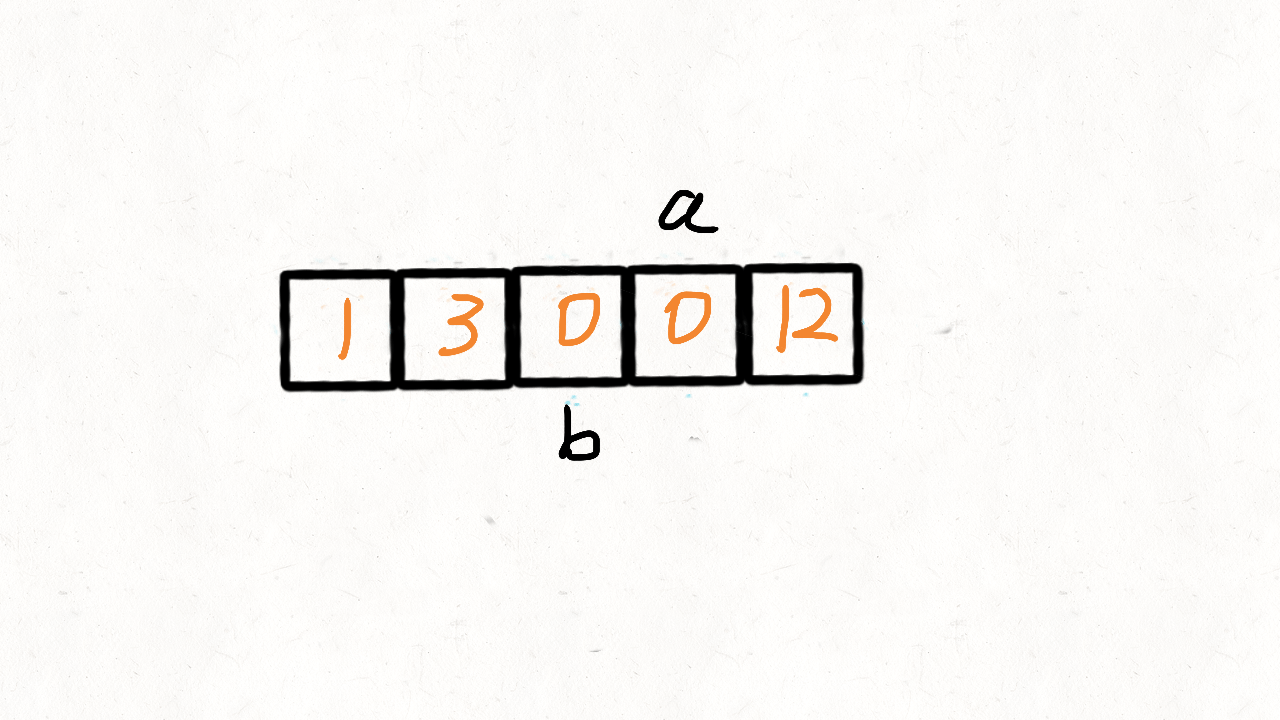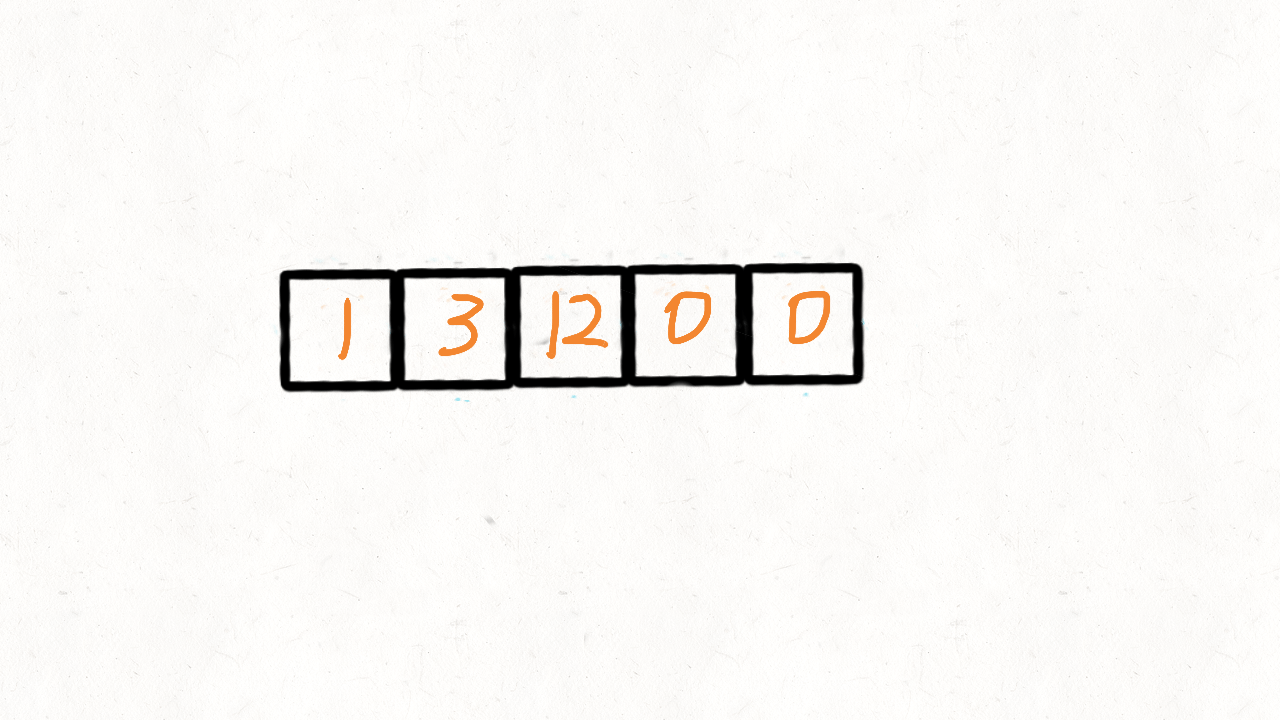题目:就是给你一个大数组,然返回和最大的小数组
思路:
前缀和
然后线性更新res= curPreSum - minPreSum,然后更新minPreSum
注意:
res的初始化
以及前缀和数组的初始值是0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ) return nums[0 ]; int []preSum = getPreSum(nums); int minPreSum=0 ; int res=Integer.MIN_VALUE;; for (int i=1 ;i<=nums.length;i++){ res = Math.max(res,preSum[i]-minPreSum); minPreSum = Math.min(preSum[i],minPreSum); } return res; } public int [] getPreSum(int []nums){ int []res =new int [nums.length+1 ]; res[0 ]=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=nums.length;i++){ res[i]=nums[i-1 ]+res[i-1 ]; } return res; } }
题目:从一个部分有序的数组中以logN的时间复杂度找数
思路:
有序中找东西就应该想到用二分查找,部分有序也是如此
部分有序就对此进行拆分嘛,分类讨论,左有序,还是右序
然后在各自的有序区域内进行搜索
https://chatgpt.com/s/t_68c997c4d3948191a4497c009540388e
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public int search (int [] nums, int target) { int l = 0 ; int r = nums.length - 1 ; while (l <= r) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] == target) { return mid; } if (nums[mid] >= nums[l]) { if (target >= nums[l] && target <= nums[mid]) { r = mid - 1 ; } else l = mid + 1 ; } else { if (target <= nums[r] && target >= nums[mid]) { l = mid + 1 ; } else r = mid - 1 ; } } return -1 ; } }
扩展:
这道题要注意:如果面试官问你再旋转一次怎么做,做法还是一样的,无论旋转几次,最多只有2段递增序列
难度加强版:https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-rotate-array-lcci/description/
字节一面对这一题做了改造,如果target存在返回target,如果target不存在,返回 > target的最小值
维护一个>target的最小值
if (nums[mid] > target) {
// nums[mid] 是一个候选答案
if (ans == null || nums[mid] < ans) {
ans = nums[mid];
}
}
题目:两个有序数组,然后合并成一个
思路:
三指针+从后向前遍历,p1,p2,p3
优先级队列
排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public void merge (int [] nums1, int m, int [] nums2, int n) { int p1=m-1 ; int p2=n-1 ; int p3=m+n-1 ; while (p1>=0 &&p2>=0 ){ if (nums1[p1]>=nums2[p2]){ nums1[p3]=nums1[p1]; p1--; } else { nums1[p3]=nums2[p2]; p2--; } p3--; } while (p2>=0 ){ nums1[p3]=nums2[p2]; p3--; p2--; } while (p1>=0 ){ nums1[p3]=nums1[p1]; p3--; p1--; } } }
题目:实现最低买入,最高卖出
思路:贪心,肯定是得选最低价的天买入,维护一个最小值即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int res=0 ; int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i=0 ;i<prices.length;i++){ res=Math.max(res,prices[i]-minPrice); minPrice=Math.min(minPrice,prices[i]); } return res; } }
https://leetcode-cn.com/circle/article/qiAgHn/,这篇文章讲的很通俗易懂,把几种情形都包括了
题目:顺时针螺旋顺序遍历二维数组
思路:
维护四个变量,然后模拟四个方向,通过 i 指针for循环遍历
注意边界问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import java.util.*;class Solution { public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length; int n = matrix[0 ].length; int up = 0 , down = m - 1 ; int left = 0 , right = n - 1 ; List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); while (left <= right && up <= down) { for (int i = left; i <= right && res.size() < m * n; i++) { res.add(matrix[up][i]); } for (int i = up + 1 ; i <= down - 1 && res.size() < m * n; i++) { res.add(matrix[i][right]); } for (int i = right; i >= left && res.size() < m * n; i--) { res.add(matrix[down][i]); } for (int i = down - 1 ; i >= up + 1 && res.size() < m * n; i--) { res.add(matrix[i][left]); } left++; right--; up++; down--; } return res; } }
题目:把多个区间,如果重叠的,就合并成多个
思路:
左端点进行排序
初始化List<int[]> tempList
然后再比较Cur区间左断点是否小于前一个区间的右断点,是的话就更新tempList里的前一个区间的右断点,不是就加入tempList
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals,(iv1,iv2)->(iv1[0 ]-iv2[0 ])); List<int []> temp=new ArrayList <>(); for (int []interval:intervals){ int size=temp.size(); if (size>0 &&interval[0 ]<=temp.get(size-1 )[1 ]){ temp.get(size-1 )[1 ]=Math.max(interval[1 ],temp.get(size-1 )[1 ]); } else temp.add(interval); } return temp.toArray(new int [temp.size()][2 ]); } }
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
题目:找凹进去最多的区域
思路:
什么决定了雨水最多能装多少,即最高左边界,最高右边界
OK,明白以上两点,我们就可以通过双指针来遍历,找出最高左边界,以及右边界
但实际雨水能装多少,还得决定于这段区间内的空格有多少,如何更新求出空格个数呢?
最高边界-当前位置高度即 可以装水的空格
最高边界是哪个边界?短板效应,即能装多少水取决于最短的最高边界
维护一个res,res+=当前位置装水空格
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int leftMax=0 ; int rightMax=0 ; int r=height.length-1 ; int l=0 ; int res=0 ; while (l<r){ leftMax=Math.max(leftMax,height[l]); rightMax=Math.max(rightMax,height[r]); int water= leftMax<rightMax? leftMax-height[l++]:rightMax-height[r--]; res+=water; } return res; } }
看不懂,先摆着
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public double findMedianSortedArrays (int [] A, int [] B) { int m = A.length, n = B.length; if (m > n) return findMedianSortedArrays(B, A); int left = 0 , right = m; int halfLen = (m + n + 1 ) / 2 ; while (left <= right) { int i = (left + right) / 2 ; int j = halfLen - i; int A_left = (i == 0 ) ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : A[i-1 ]; int A_right = (i == m) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : A[i]; int B_left = (j == 0 ) ? Integer.MIN_VALUE : B[j-1 ]; int B_right = (j == n) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : B[j]; if (A_left <= B_right && B_left <= A_right) { int maxLeft = Math.max(A_left, B_left); if ((m + n) % 2 == 1 ) return maxLeft; int minRight = Math.min(A_right, B_right); return (maxLeft + minRight) / 2.0 ; } else if (A_left > B_right) right = i - 1 ; else left = i + 1 ; } return 0.0 ; } }
题目:给你一个数组,该数组构成一个数字,找到比该数字大的最小值,且该最小值里数必须是数组里面的
arr =
例如,arr = [1,2,3] 的下一个排列是 [1,3,2] 。
必须原地 修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
开背吧
思路:
纯纯找规律
从右到左 找到递增的边界。eg:[1,2,4,3,1] 那边边界就是2,我们mark为x
然后还是从右到左找到 x 右边最小大于x的数 y。eg:[1,2,4,3,1] y为3
然后交换x和y的位置。eg:[1,2,4,3,1] —> [1,3,4,2,1]
reverse(原x位置,n-1),如果第二步找不到x即x=-1,然后就直接跳这一步。eg:[1,2,4,3,1] —> [1,3,1,2,4]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { public void nextPermutation (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int i = n - 2 ; while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1 ]) { i--; } if (i >= 0 ) { int j = n - 1 ; while (nums[j] <= nums[i]) { j--; } swap(nums, i, j); } reverse(nums, i + 1 , n - 1 ); } private void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; } private void reverse (int [] nums, int left, int right) { while (left < right) { swap(nums, left++, right--); } } } 作者:灵茶山艾府 链接:https: 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
上一个排列解法只需要改变两点:1.大于号换成小于号2.排降序
题目:目标数据[1,2,3,4,5,6……] ,让你找出缺失的第一个正数
思路:
先把有的整理一遍,寻找i这个位置上对的人 nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1]
然后for循环找出来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int firstMissingPositive (int [] nums) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= nums.length && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1 ]) { int temp = nums[nums[i] - 1 ]; nums[nums[i] - 1 ] = nums[i]; nums[i] = temp; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != i + 1 ) { return i + 1 ; } } return nums.length + 1 ; } }
思路:
//1.从前序遍历里确定根节点
PS:md是真的晕递归啊啊,为什么学了两年还是晕。。。。你理解递归不要陷入细节,先明白方法返回的是什么!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { int n = preorder.length; if (n == 0 ) { return null ; } int leftSize = getLeftSize(inorder, preorder[0 ]); int [] pre1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, 1 , 1 + leftSize); int [] pre2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, 1 + leftSize, n); int [] in1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 0 , leftSize); int [] in2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 1 + leftSize, n); TreeNode left = buildTree(pre1, in1); TreeNode right = buildTree(pre2, in2); return new TreeNode (preorder[0 ], left, right); } public int getLeftSize (int [] order, int x) { for (int i = 0 ;; i++) { if (order[i] == x) { return i; } } } }
思路:
回溯三部曲
做的时候脑子要有回溯树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [] (startIndex=0 ) / | \ [1 ] [2 ] [3 ] (分别选择 1 ,2 ,3 ) / \ / \ \ [1 ,2 ] [1 ,3 ] [2 ,3 ] ··· ··· (继续往右走) / [1 ,2 ,3 ] (完整路径)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ) { return res; } dfs(nums, 0 ); return res; } public void dfs (int [] nums, int startIndex) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) { path.add(nums[i]); dfs(nums, i + 1 ); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } }
时间复杂度 O(N*N)
思路:
二分找左右边界
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution { public int [] searchRange(int [] nums, int target) { int leftBorder=leftBorder(nums,target); int rightBorder=rightBorder(nums,target); if (leftBorder==-1 &&rightBorder==-1 ){ return new int []{leftBorder,rightBorder}; } else return new int []{leftBorder+1 ,rightBorder-1 }; } public int leftBorder (int []nums,int target) { int left=0 ; int right=nums.length-1 ; int leftBorder=-1 ; while (left<=right){ int mid=left+(right-left)/2 ; if (nums[mid]==target){ right=mid-1 ; leftBorder=right; } else if (nums[mid]<target){ left=mid+1 ; } else if (nums[mid]>target){ right=mid-1 ; } } return leftBorder; } public int rightBorder (int []nums,int target) { int left=0 ; int right=nums.length-1 ; int rightBorder=-1 ; while (left<=right){ int mid=left+(right-left)/2 ; if (nums[mid]==target){ left=mid+1 ; rightBorder=left; } else if (nums[mid]<target){ left=mid+1 ; } else if (nums[mid]>target){ right=mid-1 ; } } return rightBorder; } }
题目:给一个数组,然后给一个target,让你求和等于target的 数组里的数字组合,每个数字可重复取
思路:
回溯
重复取怎么处理呢 dfs(candidates,target,i);不是i+1, i就表示可以重复取。然后用sum>target来控制 超过就return
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); int sum = 0 ; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { dfs(candidates,target,0 ); return res; } public void dfs (int []candidates,int target,int startIndex) { if (sum == target){ res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i=startIndex;i<candidates.length;i++){ if (sum > target) break ; sum += candidates[i]; path.add(candidates[i]); dfs(candidates,target,i); sum -= path.remove(path.size()-1 ); } } }
要考虑去重吗?
题目
思路:
多条路径求最小和的,可以考虑dfs算法,但很遗憾,时间复杂度2的m+n 次方,超时了
动态规划。理清数组元素含义,以及当前状态是怎么由前面的状态推导过来的
dfs:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int sum = 0 ; int n, m; int [][] dir = {{0 ,1 },{1 ,0 }}; public int minPathSum (int [][] grid) { n = grid.length; m = grid[0 ].length; dfs(grid, 0 , 0 , 0 ); return res; } public void dfs (int [][] grid, int x, int y, int currentSum) { if (x >= n || y >= m) return ; currentSum += grid[x][y]; if (x == n-1 && y == m-1 ) { res = Math.min(res, currentSum); return ; } dfs(grid, x+1 , y, currentSum); dfs(grid, x, y+1 , currentSum); } }
动态规划
美团一面,写完要求在源码基础上生成路径?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public int minPathSum (int [][] grid) { int n = grid.length; int m = grid[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [n][m]; String[][] path = new String [n][m]; dp[0 ][0 ] = grid[0 ][0 ]; path[0 ][0 ] = "(0,0)" ; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { dp[i][0 ] = dp[i-1 ][0 ] + grid[i][0 ]; path[i][0 ] = path[i-1 ][0 ] + " -> (" + i + "," + 0 + ")" ; } for (int j = 1 ; j < m; j++) { dp[0 ][j] = dp[0 ][j-1 ] + grid[0 ][j]; path[0 ][j] = path[0 ][j-1 ] + " -> (" + 0 + "," + j + ")" ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < m; j++) { if (dp[i-1 ][j] < dp[i][j-1 ]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i-1 ][j] + grid[i][j]; path[i][j] = path[i-1 ][j] + " -> (" + i + "," + j + ")" ; } else { dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1 ] + grid[i][j]; path[i][j] = path[i][j-1 ] + " -> (" + i + "," + j + ")" ; } } } System.out.println("Path: " + path[n-1 ][m-1 ]); return dp[n-1 ][m-1 ]; }
题目:从一没排好序的数组里找出 最长的连续序列 如 1,2,3,4
思路:
hashset,for x 然后以x为开头搜连续段,后续for 时候如果遇到连续段里的就 continue 。即哈希set,每次搜索一个数搜完一个连续段,后面在遇到连续段中的直接跳过。
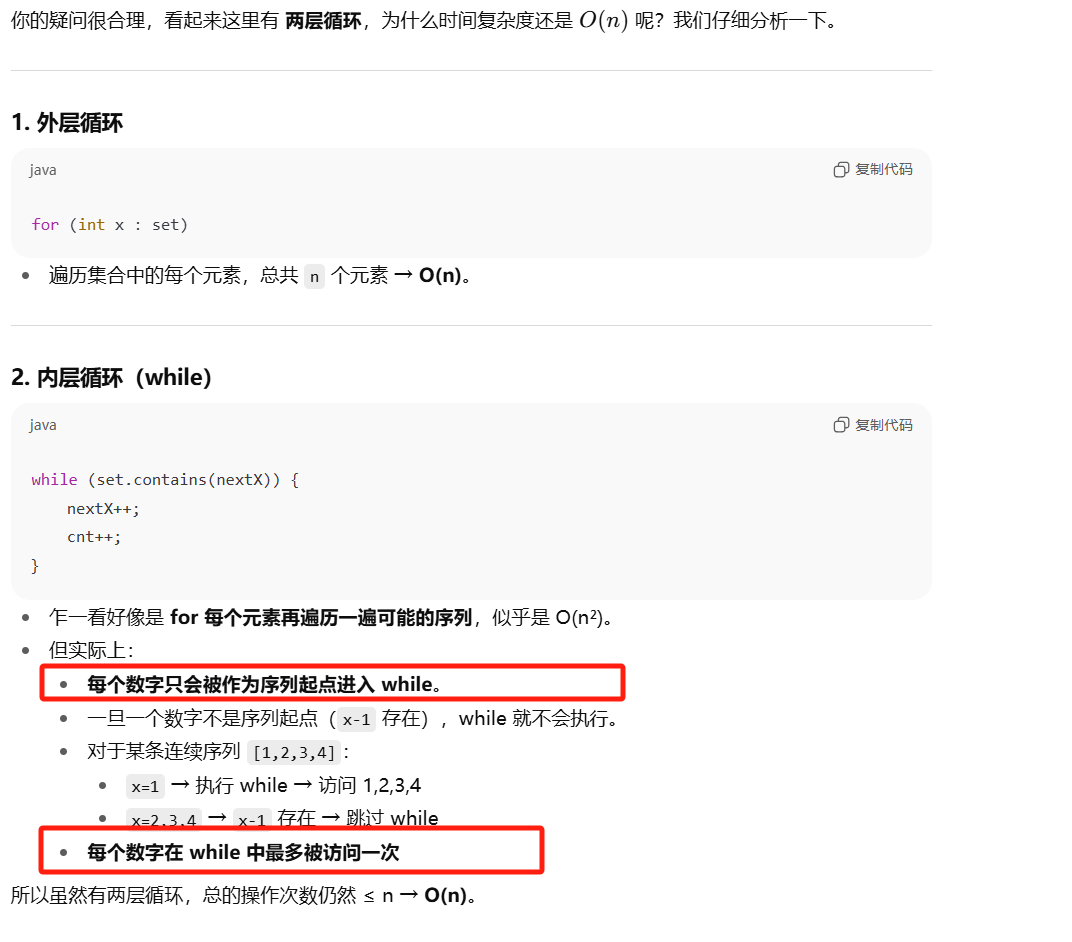
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); for (int i : nums) { set.add(i); } int res = 0 ; for (int x : set) { if (set.contains(x - 1 )) continue ; int cnt = 1 ; int nextX = x + 1 ; while (set.contains(nextX)) { nextX++; cnt++; } res = Math.max(res, cnt); } return res; } }
时间复杂度:O N,因为每个元素只被访问了一次
思路:
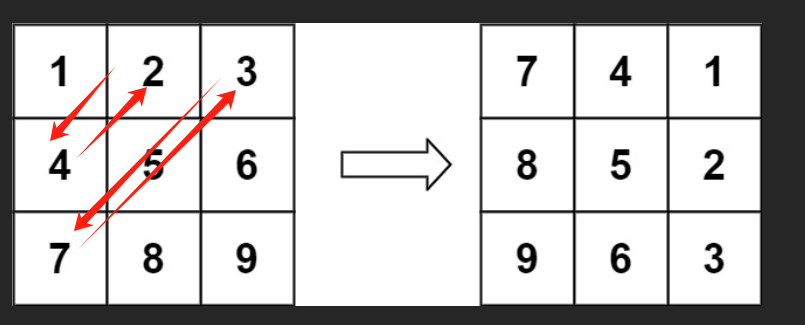
先交换行(上下倒转),然后转置( 转置操作:matrix[i][j] ↔ matrix[j][i])
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public void rotate (int [][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length - 1 ; int m = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= n/2 ; i++) { int [] temp = matrix[i]; matrix[i] = matrix[n - i]; matrix[n - i] = temp; } for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j <= m; j++) { int temp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i] = temp; } } } }
转置:
思路:
就是dfs,模版题,没啥好说的,需要注意一下这种情况因为是四面八方都可以走,那就得记录走过的位置或者说 for循环入口其实导向是同一块岛屿
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { int area = 0 ; int res = 0 ; public int maxAreaOfIsland (int [][] grid) { for (int i = 0 ; i < grid.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < grid[0 ].length; j++) { area = 0 ; dfs(grid, i, j); res = Math.max(res, area); } } return res; } public void dfs (int [][] grid, int x, int y) { if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= grid.length || y >= grid[0 ].length) { return ; } if (grid[x][y] != 1 ) { return ; } if (grid[x][y] == 1 ) area++; grid[x][y] = -1 ; dfs(grid, x + 1 , y); dfs(grid, x, y + 1 ); dfs(grid, x, y - 1 ); dfs(grid, x - 1 , y); } }
题目:找出山峰,返回山峰的索引
思路:二分查找,分情况讨论
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 if (nums[mid] < nums[mid + 1 ]) { l = mid + 1 ; } else { r = mid - 1 ; }
图解:162. 寻找峰值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int findPeakElement (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ) return 0 ; if (nums[nums.length - 1 ] > nums[nums.length - 2 ]) { return nums.length - 1 ; } if (nums[0 ] > nums[1 ]) { return 0 ; } int l = 0 ; int r = nums.length - 1 ; while (l <= r) { int mid = (r + l) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] < nums[mid + 1 ]) { l = mid + 1 ; } else { r = mid - 1 ; } } return l; } }
思路:
map
空间复杂度O(1)的解法:摩尔投票
题目:长度最小的和为k的子数组
思路:
思路:
双指针,i0,i
记录0元素的位置i0,i。如果nums[i]为非0元素,就与其交换,然后i0++
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int i0 = 0 ; for (; i0 < nums.length; i0++) { if (nums[i0] == 0 ) { break ; } } for (int i = i0 + 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != 0 ) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[i0]; nums[i0] = temp; i0++; } } } }
题目:在部分有序数组中找到最小值
思路:
看到log N的算法,就得想到二分
根据mid和nums.length元素比较 得出最小值是在右边还是在左边
[3,4,5,1,2]:最小值在右边
[1 2 3 4 5]:最小值在左边
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int findMin (int [] nums) { int l = 0 ; int r = nums.length - 1 ; while (l <= r) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] > nums[nums.length - 1 ]) { l = mid +1 ; } else { r = mid -1 ; } } return nums[l]; } }
先升序再降序的数组,找到最大值 参考寻找峰值
思路:
dfs+回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { int offset = -1 ; boolean [][] visited; public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { visited = new boolean [board.length][board[0 ].length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < board.length; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < board[0 ].length; j++) { if (dfs(board, i, j, word, 0 )) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean dfs (char [][] board, int x, int y, String word, int offset) { if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= board.length || y >= board[0 ].length) { return false ; } if (visited[x][y]) return false ; if (board[x][y] != word.charAt(offset)) { return false ; } if (offset == word.length() - 1 ) return true ; visited[x][y] = true ; boolean found = dfs(board, x, y + 1 , word, offset + 1 ) || dfs(board, x + 1 , y, word, offset + 1 ) || dfs(board, x, y - 1 , word, offset + 1 ) || dfs(board, x - 1 , y, word, offset + 1 ); visited[x][y] = false ; return found; } }
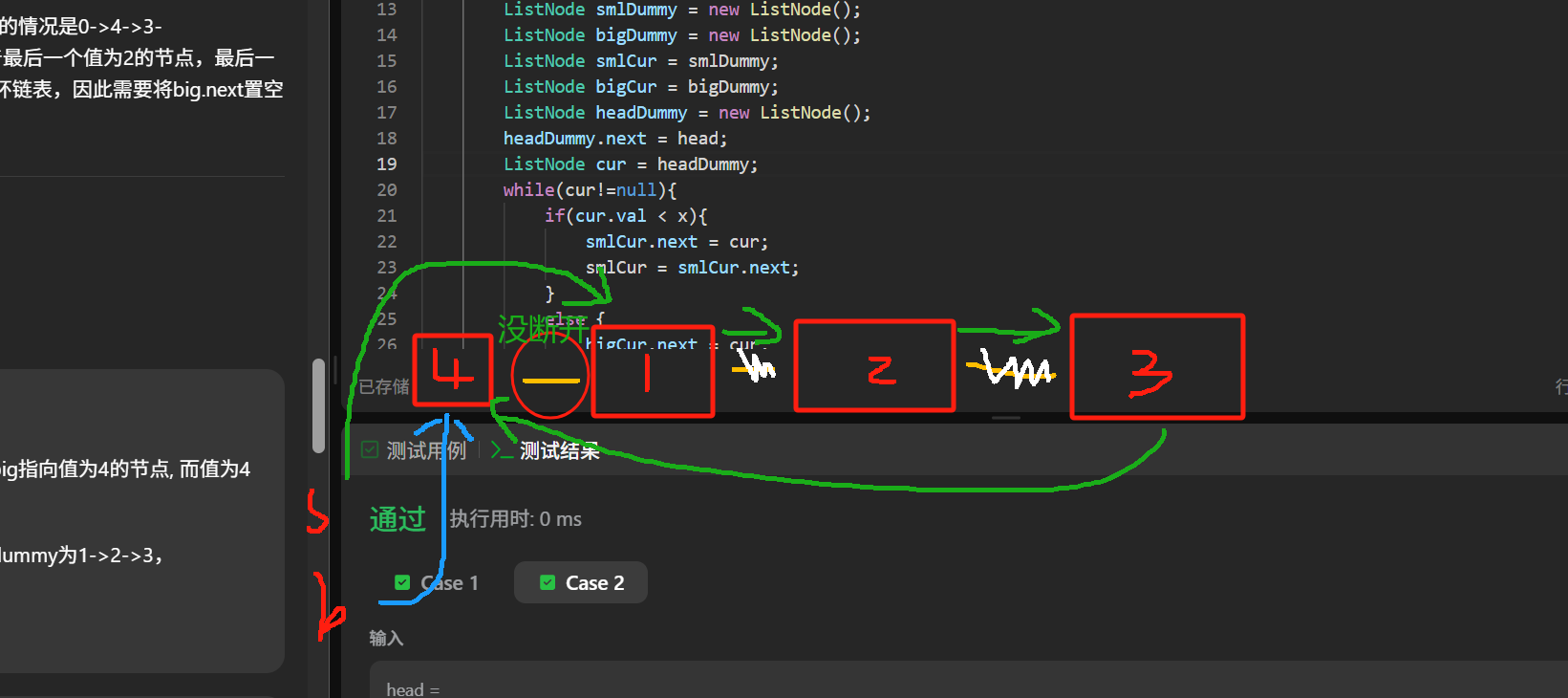
思路:
双指针,sml,big
if cur < x 加入sml,else 加入big
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public ListNode partition (ListNode head, int x) { ListNode smlDummy = new ListNode (); ListNode bigDummy = new ListNode (); ListNode smlCur = smlDummy; ListNode bigCur = bigDummy; ListNode cur = head; while (cur!=null ){ if (cur.val < x){ smlCur.next = cur; smlCur = smlCur.next; } else { bigCur.next = cur; bigCur = bigCur.next; } cur = cur.next; } smlCur.next = bigDummy.next; bigCur.next = null ; return smlDummy.next; } }
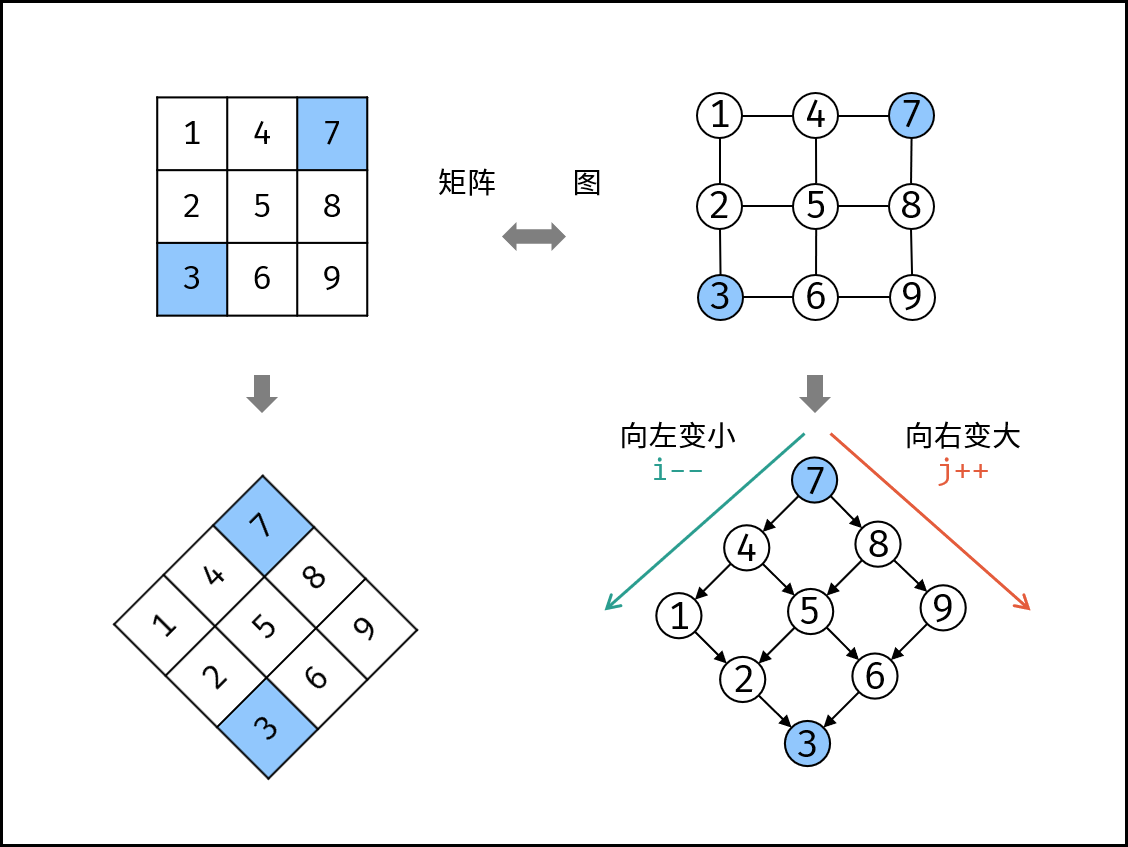
思路:旋转45度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public boolean searchMatrix (int [][] matrix, int target) { int i = matrix.length - 1 ; int j = 0 ; while (i >= 0 && j < matrix[0 ].length){ if (matrix[i][j] > target){ i--; } else if (matrix[i][j] < target){ j++; } else return true ; } return false ; } }
思路:
暴力,两层for循环
是不可以搞前缀积的!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int maxProduct (int [] nums) { int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ int sub = 1 ; for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++){ sub = sub * nums[j]; res = Math.max(res, sub); } } return res; } }
动态规划
维护当前最大值和当前最小值
解释:当前最大值和当前最小值是指什么?
变量
更严谨的定义
curMax以 nums[i]
curMin以 nums[i]
因为当遇到负数时,要乘上负数时,当前最大值会变成当前最小值,当前最小值会变成当前最大值
如果一直遇到整数,那么不断curMax * curNum[] 就好了
如果遇到了 0,这时候就会自动断开了,curMax = 0, curMin = 0(即重开了)
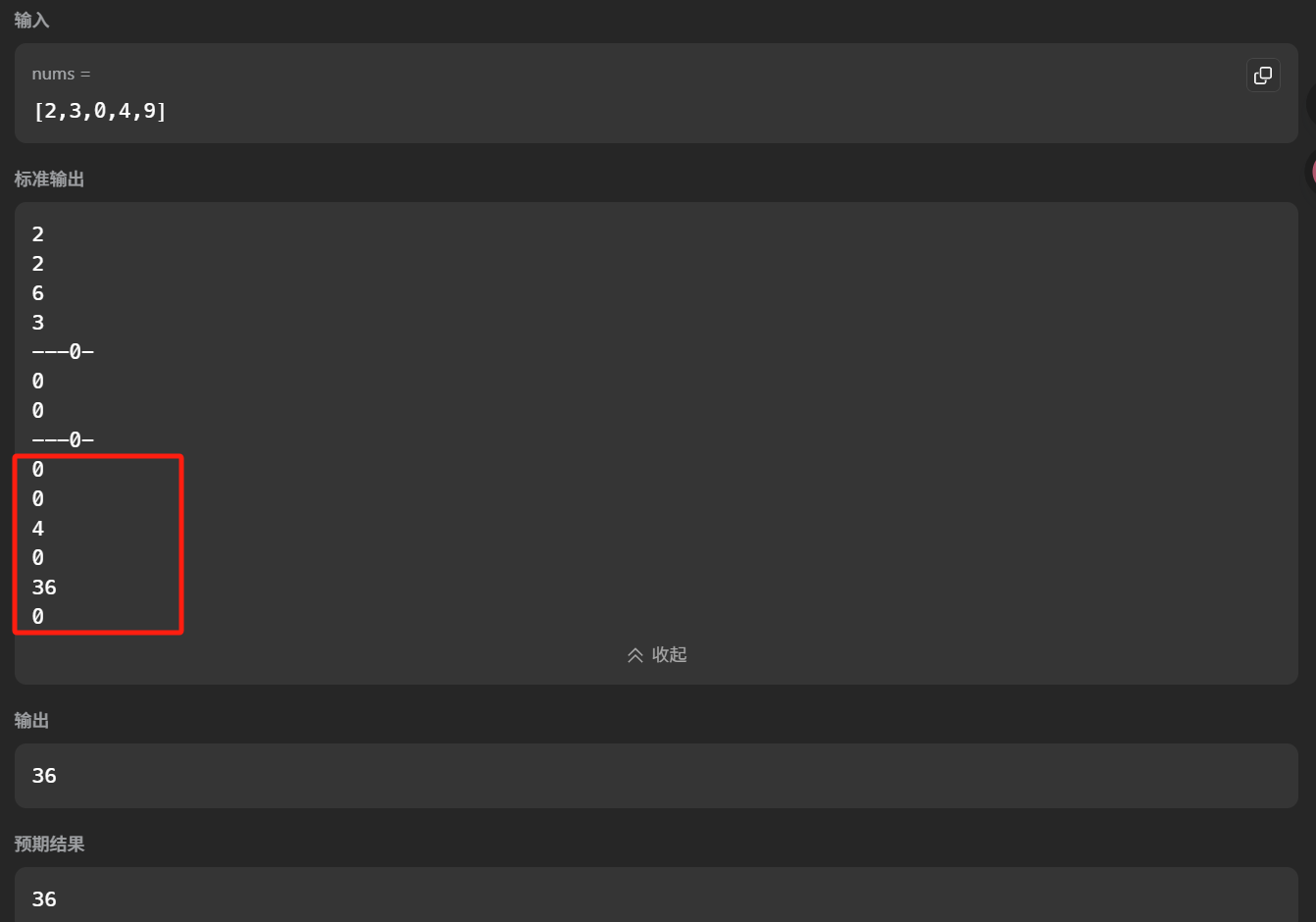
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public int maxProduct (int [] nums) { int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int curMax = 1 ; int curMin = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] < 0 ) { int temp = curMax; curMax = curMin; curMin = temp; } curMax = Math.max(curMax * nums[i], nums[i]); curMin = Math.min(curMin * nums[i], nums[i]); if (nums[i] == 0 ){ System.out.println("---0-" ); System.out.println(curMax); System.out.println(curMin); System.out.println("---0-" ); } System.out.println(curMax); System.out.println(curMin); res = Math.max(curMax, res); } return res; } }
字节腾讯,还要输出这个数组
维护bestStart bestEnd,然后如果nums[i] > curMax 就会开始重新计数了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public int maxProduct (int [] nums) { int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int curMax = 1 ; int curMin = 1 ; int start = 0 , bestStart = 0 , bestEnd = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] < 0 ) { int temp = curMax; curMax = curMin; curMin = temp; } if (curMax * nums[i] < nums[i]) { curMax = nums[i]; start = i; } else curMax = curMax * nums[i]; curMin = Math.min(curMin * nums[i], nums[i]); if (res < curMax) { res = curMax; bestStart = start; bestEnd = i; } } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, bestStart, bestEnd + 1 ))); return res; } }
思路:两种做法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public boolean canJump (int [] nums) { if (nums.length <= 1 ) return true ; int k = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= k; i++){ k = Math.max(k, nums[i] + i); if (k >= nums.length - 1 ){ return true ; } } return false ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public boolean canJump (int [] nums) { if (nums.length <= 1 ){ return true ; } int k = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > k) return false ; k = Math.max(k, i + nums[i]); System.out.println("当前下标:" + i + "最远位置:" + k); } return true ; } }
两种做法:
动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int jump (int [] nums) { if (nums.length <= 1 ) return nums.length - 1 ; int n = nums.length; int []dp = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(dp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); dp[0 ] = 0 ; dp[1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ int k = i + nums[i]; if ( k > nums.length - 1 ){ k = nums.length - 1 ; } dp[k] = Math.min(dp[k], dp[i] + 1 ); for (int j = i + 1 ; j < k + 1 ; j++){ dp[j] = Math.min(dp[k], dp[j]); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp)); } return dp[n - 1 ]; } }
时间复杂度 = O(n²),空间复杂度 = O(n)
贪心
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int jump (int [] nums) { int steps = 0 ; int end = 0 ; int farthest = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++) { farthest = Math.max(farthest, i + nums[i]); if (i == end) { steps++; end = farthest; } } return steps; } }
思路:
双指针
贪心思路: 木桶容量由短板决定, 移动长板的话, 水面高度不可能再上升 , 而宽度变小了, 所以只有通过移动短板, 才有可能使水位上升.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxArea (int[] height ) { int l = 0 ; int r = height.length - 1 ; int res = Integer .MIN_VALUE ; while (l <= r){ int h = Math .min (height[l], height[r]); res = Math .max (res, h * (r - l)); if (height[l] > height[r]){ r--; } else l++; } return res; } }
思路:
最简单的做法,即先排序,然后比对,从左,从右,找第一个不同的元素,然后len = right - left + 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int findUnsortedSubarray (int [] nums) { int [] newNums = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0 , nums.length); Arrays.sort(newNums); int l = 0 ; int r = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ;i < newNums.length; i++){ if (newNums[i] != nums[i]){ l = i; break ; } } for (int i = newNums.length - 1 ;i >= 0 ; i--){ if (newNums[i] != nums[i]){ r = i; break ; } } return r - l + 1 > 0 ? r - l + 1 : 0 ; } }
计数排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { public int findUnsortedSubarray (int [] nums) { int [] newNums = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0 , nums.length); sort(newNums); int l = 0 ; int r = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ;i < newNums.length; i++){ if (newNums[i] != nums[i]){ l = i; break ; } } for (int i = newNums.length - 1 ;i >= 0 ; i--){ if (newNums[i] != nums[i]){ r = i; break ; } } return r - l + 1 > 0 ? r - l + 1 : 0 ; } public void sort (int []nums) { int MAX = 100000 ; int [] counter = new int [MAX * 2 + 4 ]; int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i: nums){ min = Math.min(i, min); max = Math.max(i, max); counter[i + MAX]++; } int idx = 0 ; for (int i = min; i <= max; i++){ int count = counter[i + MAX]; while (count > 0 ){ nums[idx] = i; count--; idx++; } } } }
思路:
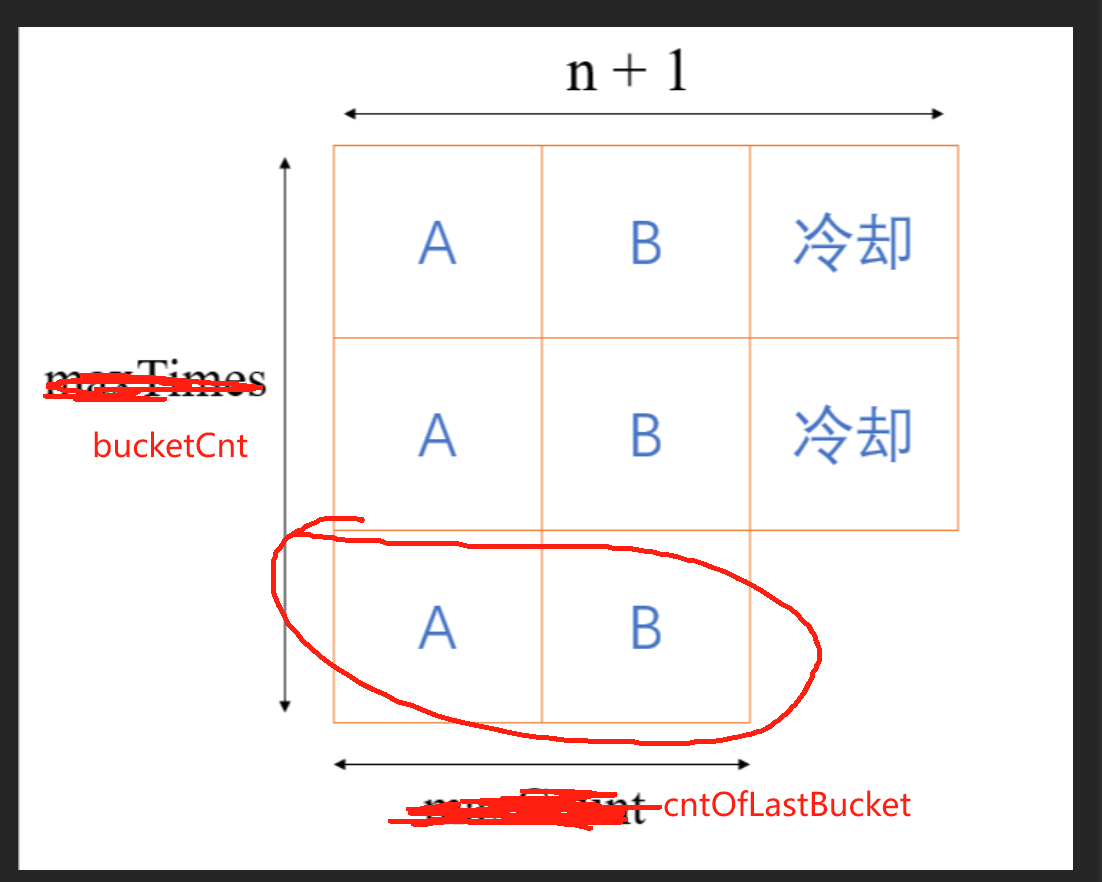
贪心:很容易想到就是 先安排出现次数最多的任务,然后让这个任务之间的间隔刚好为N
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public int leastInterval (char [] tasks, int n) { Map<Character,Integer> counter = new HashMap (); for (char c: tasks){ counter.put(c, counter.getOrDefault(c, 0 ) + 1 ); } int max = 0 ; char cMax = '*' ; for (char c: counter.keySet()){ if (counter.get(c) > max) { cMax = c; max = counter.get(c); } } int bucketCnt = max; int cntOflastBucket = 0 ; for (char c: counter.keySet()){ if (counter.get(c) == max) cntOflastBucket++; } return Math.max((bucketCnt - 1 ) * (n + 1 ) + cntOflastBucket, tasks.length); } }
同缺失的第一个正数
思路:
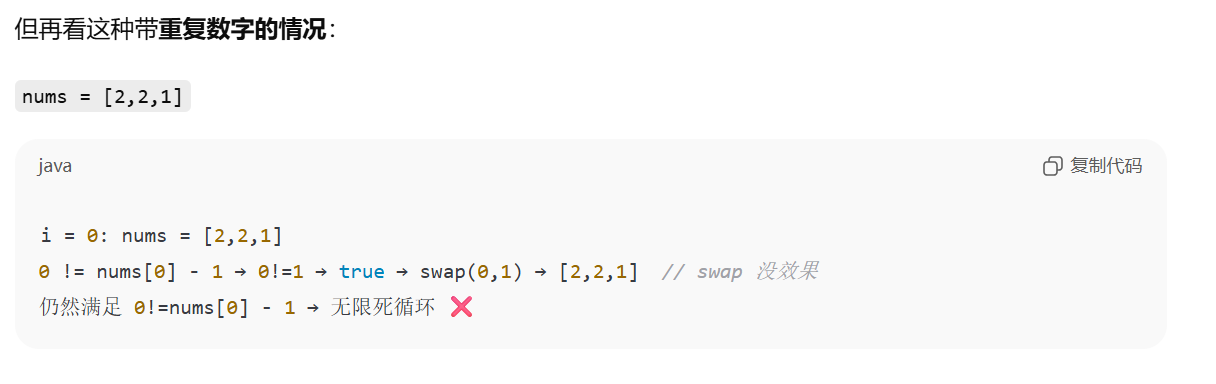
交换到正确的位置上
[1,2,3] –> nums[i] == nums[nums[i] - 1],即nums[0] == nums[1 - 1]。为什么不能写成 i=nums[i] - 1?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution { public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers (int [] nums) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ System.out.println(i); System.out.println(nums[i] +"::::::::::::" + nums[nums[i] - 1 ]); while (nums[i] <= nums.length && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1 ]){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums)); System.out.println(i + ":::" + (nums[i] -1 )); swap(nums, i, nums[i] - 1 ); } } List<Integer> res = new ArrayList (); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (nums[i] != i + 1 ) res.add(i + 1 ); } return res; } public void swap (int []nums, int i,int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } }
先排序,先按p[0] 降序 and p[1] 升序。
:::info楼主的解释很棒!但是这里稍微有点没有解释清楚,“按照第二个元素正向排序,我们希望 k 大的尽量在后面,减少插入操作的次数。”不止是为了减少插入次数,也是为了保证正确性。 举个例子,在身高一样,k不一样的时候,譬如[5,2]和[5,3], 对于最后排完的数组,[5,2]必然在[5,3]的前面。所以如果遍历的时候[5,3]在前面,等它先插入完,这个时候它前面会有3个大于等于它的数组对,遍历到[5,2]的时候,它必然又会插入[5,3]前面(因为它会插入链表索引为2的地方),这个时候[5,3]前面就会有4个大于等于它的数组对了,这样就会出错。
:::
然后巧用 add(index,n)实现插队
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int [][] reconstructQueue(int [][] people) { Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> { return a[0 ] == b[0 ] ? a[1 ] - b[1 ] : b[0 ] - a[0 ]; } ); List<int []> res = new ArrayList (); for (int []p: people) { System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p)); res.add(p[1 ], p); } System.out.println("////////////" ); for (int []p: res) { System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p)); } return res.toArray(new int [people.length][2 ]); } }
思路
前缀积,后缀积
Map<Integer,Integer> front:k:当前元素index。v:包含当前元素的区间积,元素之前的积即map.getIOrDefault(i - 1, 1) * curNum
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import java.util.*;class Solution { public int [] productExceptSelf(int [] nums) { int [] ans = new int [nums.length]; Map<Integer, Integer> front = new HashMap <>(); Map<Integer, Integer> back = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { front.put(i, front.getOrDefault(i - 1 , 1 ) * nums[i]); } for (int i = nums.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { back.put(i, back.getOrDefault(i + 1 , 1 ) * nums[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { int left = front.getOrDefault(i - 1 , 1 ); int right = back.getOrDefault(i + 1 , 1 ); ans[i] = left * right; } return ans; } }