字符串
最长回文子串
思路:见代码
1 | class Solution { |
有效的括号
思路:
- 遇到右括号入栈,遇到左括号则与栈顶比较
1 | class Solution { |
字符串相加
题目:大数相加
思路:
- 倒序相加,p1,p2从后面遍历字符串,然后at(p1) 和 at(p2) 进行相加,若p1 or p2 <0 就at(p) =0
- 相加过程:sum = at(p1) +at(p2) + pos(上一次运算进的位),然后当前位置的相加后的值 = sum%10,下一次进位 sum/10
- 后面如果出现 9+1这边,while结束后 if(pos > 1) append(1)
- 最后结果倒置 reverse()
1 | class Solution { |
大数相减要怎么做?或者说num1 为负数呢
1 |
复原IP地址
思路:
- 第一步要要思考,当下有几种选择?
- 以 “25525511135” 为例,第一步时我们有几种选择?
- 选 “2” 作为第一个片段
- 选 “25” 作为第一个片段
- 选 “255” 作为第一个片段
- 然后第二步的时候我们又有几种选择,切第二个片段时,又面临三种选择
- 这会向下分支,形成一棵树,我们用 DFS 去遍历所有选择,必要时提前回溯。
- 以 “25525511135” 为例,第一步时我们有几种选择?
因为某一步的选择可能是错的,得不到正确的结果,不要往下做了。撤销最后一个选择,回到选择前的状态,去试另一个选择。
回溯的第一个要点:选择,它展开了一颗空间树。
- 第二步思考,有什么约束
约束条件限制了当前的选项,这道题的约束条件是:
不能有前导0,截取的字符串不能比255大,字符串截取长度为1-3
我们应该利用这些约束条件,对其进行剪枝。
- 用这些约束进行充分地剪枝,去掉一些选择,避免搜索「不会产生正确答案」的分支。
- 第三部思考,目标是什么
什么时候应该收集结果 - 定义dfs函数
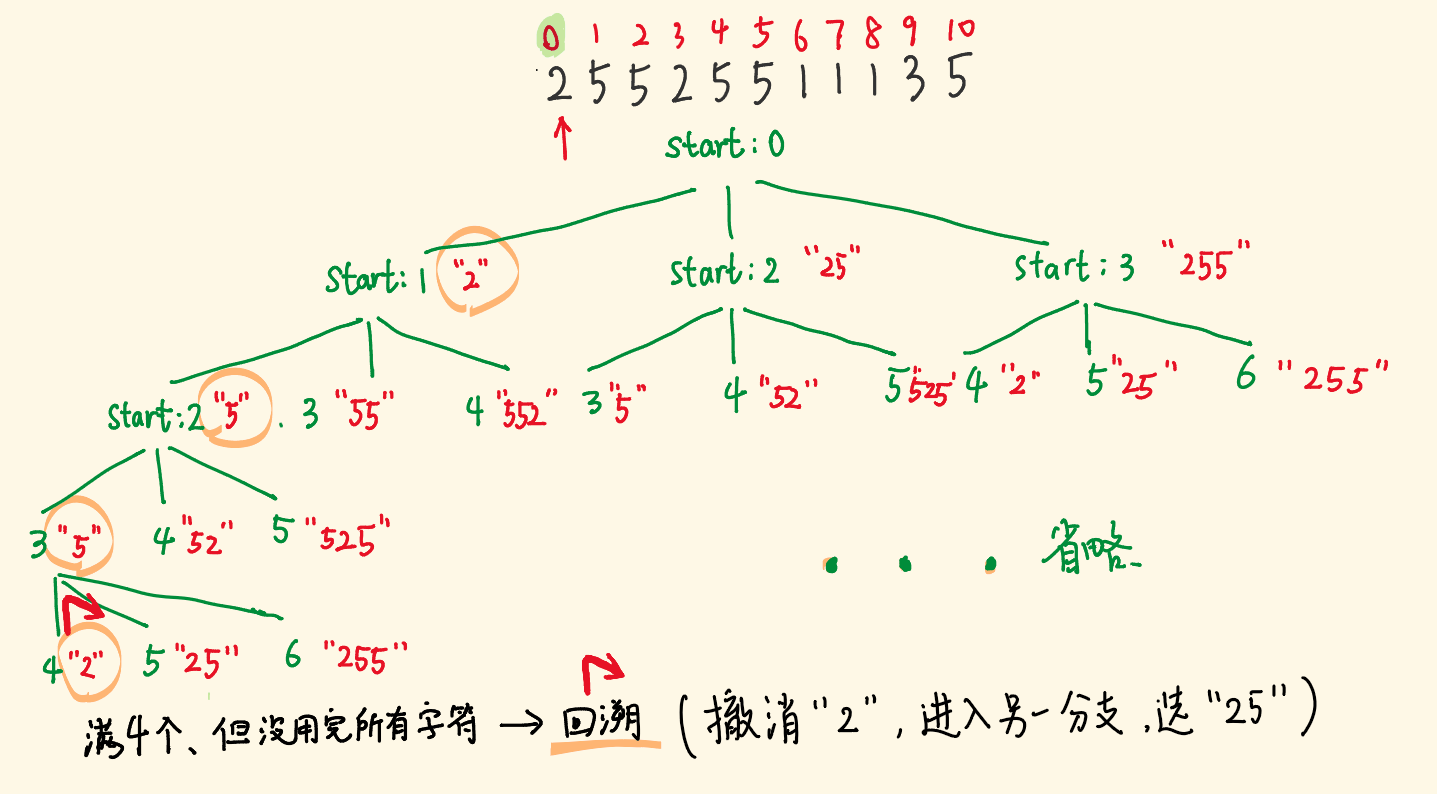
return的作用是退回上一个选择点!!!
1 | class Solution { |
比较版本号
思路:
- 分格String,用split,得到string []s
- 取两个str数组[] ,mark version
- 将s里的值装成Integer比较
1 | class Solution { |
字节2面时候遇到过,不让用已知方法(java里String#split 方法),不让分割成String数组,可以试着自己手写一个双指针的方法
括号生成[137]
思路:
- 先把树图给列举出来,思考选择(加右括号还是左括号),约束,目标
- 回溯属性,path作为参数来说,return时只带恢复现场。而不是像全局属性一样(如下下),得手动恢复现场
1 | class Solution { |
全局属性path
1 | class Solution { |

字符串转换整数 (atoi)
最长有效括号
思路:
- 找到匹配括号的下标,然后存进一个LIst
- 接下来就是转换成 寻找最长连续子序列
- 两种做法:排序后滑动窗口,时间复杂度O(NlogN)
- hashset,时间复杂度O(N)
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
字符串相乘[116]
思路:
- 直接背诵,debug一遍也行
1 | class Solution { |
最小覆盖子串
题目:
思路:
1 | class Solution { |
反转字符串中的单词
思路:
- 先把所有单词挑出来
- 然后翻转 String数组
1 | class Solution { |
最长公共前缀
耻辱:快手日常侧开一面竟然脑子坏了
思路:
1.
1 | class Solution { |
验证IP地址
思路:
- 就是简单模拟
- 学到的东西:Integer.parseInt(x,进制) 可指定进制
- 可以学学正则表达式
1 | class Solution { |
基本计算器 II[67]
思路:
1 | class Solution { |
完全版,应对所有情况,即完整的计算器
1 | class Solution { |
解码方法[42]
思路:
- dfs分隔
- 但单单dfs,就超时了
- 得进行记忆化操作
1 | class Solution { |
记忆化后
1 | class Solution { |
验证回文串
思路:
- 熟悉几个API的使用
- 双指针
1 | class Solution { |
正则表达式匹配
有效的括号字符串
思路:
- 双栈,存小标
- 最后判断一下下标是否合法 eg:(* or *(
1 | class Solution { |
字母异位词分组[12]
思路:
- 字符串字典排序,然后MAP
1 | class Solution { |
交错字符串[27]
题目:
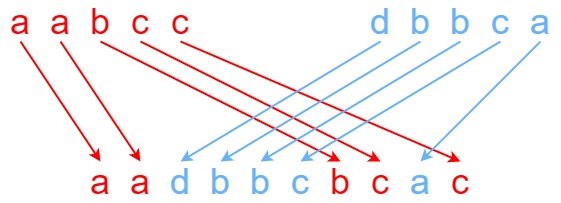
思路:
- dfs,困惑:有时候连dfs的函数都想不出来,真的逆天,没想清楚是字符串是怎么匹配的。还是得把回溯树给画出来
- 回溯时间复杂度为2^k(k为s3的长度),故得进行记忆化,来剪枝
1 | class Solution { |
补充题9. 36进制加法
思路:就是大数相加的扩展
1 |
去除重复字母
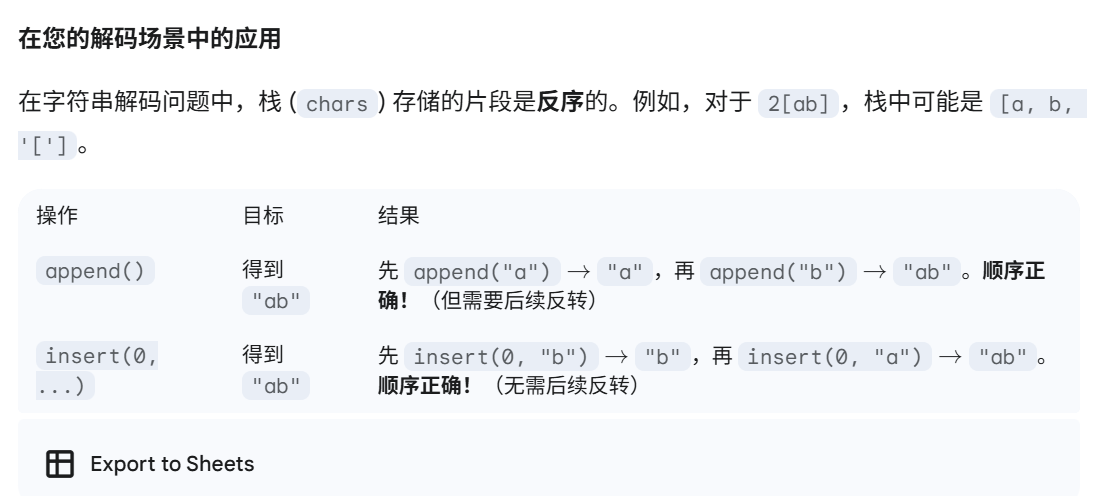
字符串解码[90]
思路
- 类似于 基本计算器,也是双栈
- 一个栈存数字,一个栈存字符。这里的 [ 就类似于 *
- 逻辑,遇到字符,遍历直到不是字符,遇到数字也是,遇到] 就 cal运算。
1 | class Solution { |
时间复杂度