题目:就是给一个str,然后让你找到无重复字符的最长子串
思路:
- 整体就是滑动窗口
- map来存储子串的字符状态
- r++ ,map不断更新,map.put() while(map.get(xx) > 1){ l++; map.put()去把map里的之前状态消掉 } res不断更新
两数之和[🔥285][易]
题目:给你一个数组,一个target。然后让你去从数组中找到能组成target的元素
思路:
- 数组 先存一遍 cache set
- 遍历一遍数组,然后 cache.contains(target - curV) 如果为true ,就更新
题目:用非递归的形式输出二叉树的中序遍历
题目:给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
输入:s = “ADOBECODEBANC”, t = “ABC”
输出:”BANC”
解释:最小覆盖子串 “BANC” 包含来自字符串 t 的 ‘A’、’B’ 和 ‘C’。
思路:
- 整体还是滑动窗口
- 维护一个map,map为t的映射表(k:字符,v:字符出现个数)。一个cnt,cnt初始化为 t的字符个数,表示还剩多少个字符可构成 t
- r++直到找到了t的第一个元素,ifxxx>0,cnt–,map[c] –
- while(cnt==0) 开始更新结果,且把最左边的东西弹出去
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
Map<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
need.put(c, need.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
int cnt = t.length();
int l = 0, r = 0;
int minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
String res = "";
for (; r < s.length(); r++) {
char cr = s.charAt(r);
if (need.containsKey(cr)) {
if (need.get(cr) > 0) cnt--;
need.put(cr, need.get(cr) - 1);
}
while (cnt == 0) {
if (r - l + 1 < minLen) {
minLen = r - l + 1;
res = s.substring(l, r + 1);
}
char cl = s.charAt(l);
if (need.containsKey(cl)) {
need.put(cl, need.get(cl) + 1);
if (need.get(cl) > 0) cnt++;
}
l++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
|
时间复杂度:O N(s.length)+M(t.length)
题目:就是给你一个source,一个target,然后找出source字符串里面的包含target所有字符的字符子串
思路:
- 整体就是滑动窗口
- 然后初始化一个 26个字母的数组 [0 1 2 ……. ]
- 长度<target.length()就跳过
- 啥时候更新结果:当上面那个数组等于 target的数组模式时就更新
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList();
int[] target = new int[26];
int[] cs = new int[26];
for (char c : p.toCharArray()) {
target[c - 'a']++;
}
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
for (; r < s.length(); r++) {
cs[s.charAt(r) - 'a']++;
if (r - l + 1 < p.length()) {
continue;
}
if (Arrays.equals(cs, target)) {
res.add(l);
}
cs[s.charAt(l) - 'a']--;
l++;
}
return res;
}
}
|
评论
评论
最热 | 最新

puffan
2021-06-23
滑动窗口O(n)
3
暂无回复
回复

一天到晚只会刷算法的疯狂javaer
2023-08-16
我直接一个滑动窗口滑滑滑
2
暂无回复
回复

Li
2022-08-19
华子实习手撕
2
暂无回复
回复

伟
2022-02-28
滑动窗口算法, 跟字符串排列思路一样
1
暂无回复
回复

Thirt33n
2024-07-09
字节三面
0
暂无回复
回复

用户OTCHR
2023-02-02
滑动窗口
0
暂无回复
回复

小号备战校招
2022-11-06
字节一面,跟567一样
0
暂无回复
回复
## [
和为K的子数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k)[🔥
70]
题目:给你一个数组,然后让你从里面找到和为k的子数组,并统计个数
思路1:
- 给出前缀和
- 转化为两数之和 即求 i(前缀和)-k的元素是否存在
思路2:
- 就是map方式的前缀和
思路3:
- 动态规划
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| class Solution {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int []preSum=getPreSum(nums);
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
int res=0;
for(int i:preSum){
if(map.containsKey(i-k)){
res+=map.get(i-k);
}
map.put(i,map.getOrDefault(i,0)+1);
}
return res;
}
public int []getPreSum(int []nums){
int []preSum=new int[nums.length+1];
preSum[0] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=nums.length;i++){
preSum[i]=preSum[i-1]+nums[i-1];
}
return preSum;
}
}
|
题目:给两个整数数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,返回 两个数组中 公共的 、长度最长的子数组的长度 。
思路:
- 滑动
题目:拷贝特殊链表节点
思路:
- 普通链表初始化
- 初始化两个MAP
- 一个记录旧链表里 节点与index的关系
- 一个记录新链表里 index与节点的关系
- 由于新旧节点 index是一样的
- 故 旧链表可以通过node.random拿到该random.index
- 再通过index拿到新链表的node
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node node=head;
Node dummyHead = new Node(0);
Node cur = dummyHead;
Map<Node,Integer> nodeMap=new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer,Node> indexMap=new HashMap<>();
int index=0;
while(node!=null){
nodeMap.put(node,index);
node=node.next;
index++;
}
node=head;
index=0;
while(node!=null){
cur.next=new Node(node.val);
cur=cur.next;
node=node.next;
indexMap.put(index,cur);
index++;
}
node=head;
cur=dummyHead.next;
while(node!=null){
cur.random=indexMap.get(nodeMap.get(node.random));
cur=cur.next;
node=node.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
|
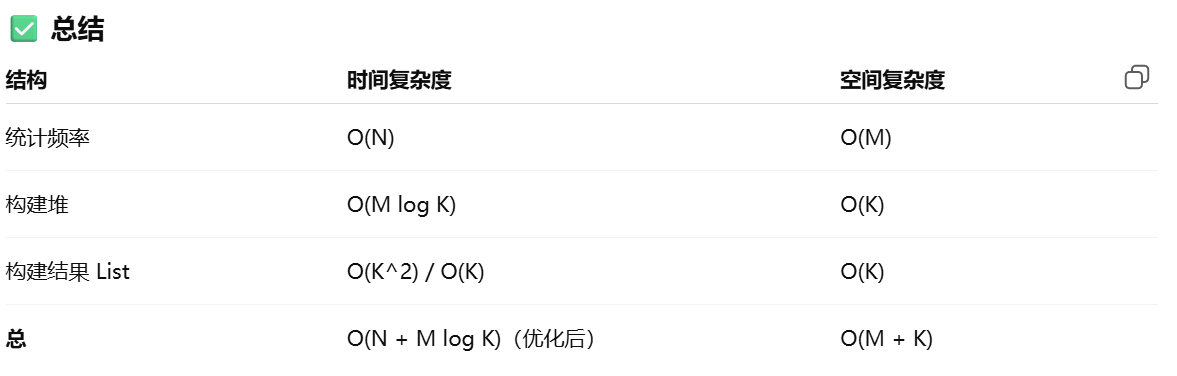
思路:hashmap统计+优先级队列维护前k个高频元素
无法单单用TreeMap排序,因为 TreeMap 只能按 key 排序,不能用value
优先级队列:
PriorityQueue
- map统计 次数
- 构造最小堆,且维护数量为k个,大于就驱逐最小的
- 然后到最后剩下的就是前k个高频元素了
Q:为什么不用最大堆?
A:最大堆,堆顶最大元素,你怎么驱逐堆低元素?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer,Integer> countMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int num : nums) {
countMap.put(num, countMap.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer,Integer>> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a,b) -> a.getValue() - b.getValue()
);
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry : countMap.entrySet()) {
heap.offer(entry);
if (heap.size() > k) {
heap.poll();
}
}
int[] res = new int[k];
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
res[i] = heap.poll().getKey();
}
return res;
}
}
|
思路:查重就用Set 或者Map!!!!!!!!!!
contains
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
HashSet<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
int length=Math.max(nums1.length,nums2.length);
HashSet<Integer> res=new HashSet<>();
for(int n:nums1){
set.add(n);
}
for(int n:nums2){
if(set.contains(n)){
res.add(n);
}
}
int []ans=new int[res.size()];
int count=0;
for(int i:res){
ans[count++]=i;
}
return ans;
}
}
|
retainAll的用法:求两个集合的交集,会把非交集的元素remove掉
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| HashSet<Integer> objects = new HashSet<>();
objects.add(1);
objects.add(2);
objects.add(3);
ArrayList<Object> objects1 = new ArrayList<>();
objects1.add(1);
objects1.add(2);
objects1.retainAll(objects);
System.out.println(objects1);
|
面试官会先问:两个数组求交集,怎么求?以及说一下时间复杂度(不允许使用编程语言自带的交集功能)。答完之后再问:如果两个数组都是非递减的,又应该怎么求?时间复杂度多少?(本人亲身经历)
思路:
- 排序 + 三指针(i [l , r])+ Set(自动去重)
- 排序 + 三指针 + 手动去重(剪枝)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Set<List<Integer>> res = new HashSet();
int n = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int l = i + 1;
int r = n - 1;
if(nums[i] > 0) break;
while(l < r){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r];
if(sum == 0){
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList();
path.add(nums[i]);
path.add(nums[l]);
path.add(nums[r]);
res.add(path);
l++;
r--;
}
else if(sum < 0) l++;
else r--;
}
}
return new ArrayList(res);
}
}
|
二数之和:哈希
三数之和:排序 + 双指针 + 剪枝
四数之和:排序 + 双指针 + 剪枝
思路:
思路:hashMap+数组
Map:k为值,v为index,这样就可以containsKey了,杜绝重复insert
数组就是用来存放元素的
并且维护一个index
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class RandomizedSet {
static int[] nums = new int[200010];
Random random = new Random();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int idx = -1;
public boolean insert(int val) {
if (map.containsKey(val)) return false;
nums[++idx] = val;
map.put(val, idx);
return true;
}
public boolean remove(int val) {
if (!map.containsKey(val)) return false;
int loc = map.remove(val);
if (loc != idx) map.put(nums[idx], loc);
nums[loc] = nums[idx--];
return true;
}
public int getRandom() {
return nums[random.nextInt(idx + 1)];
}
}
|
题目:
给定一个单词列表 words 和一个整数 k ,返回前 k 个出现次数最多的单词。
返回的答案应该按单词出现频率由高到低排序。如果不同的单词有相同出现频率, 按字典顺序 排序。
看题啊尼玛的
思路:
- hashmap统计
- 最小堆维护前k个高频单词
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class Solution {
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
Map<String, Integer> freqMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
freqMap.put(word, freqMap.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> {
if (!a.getValue().equals(b.getValue())) {
return a.getValue() - b.getValue();
} else {
return b.getKey().compareTo(a.getKey());
}
}
);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : freqMap.entrySet()) {
pq.offer(entry);
if (pq.size() > k) pq.poll();
}
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
res.add(0, pq.poll().getKey());
}
return res;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
int [] cntS =new int[26];
int [] cntT =new int[26];
for(char c: s.toCharArray()){
cntS[c-'a']++;
}
for(char c: t.toCharArray()){
cntT[c-'a']++;
}
return Arrays.equals(cntS,cntT);
}
}
|







