目录
1、路由转发
2、失败重试
3、熔断降级
4、实现过程
4.1 正常路由转发
4.2 请求重试
4.3 熔断降级
1、路由转发
路由转发**** 是网关处理完毕所有过虑逻辑之后的最后一个要执行的操作,它负责将请求最终转发到某一个指定的后端服务,这里参考 Spring Cloud Gateway 的实现方式来模拟一个路由转发过滤器
在 Spring Cloud Gateway 这一先进的微服务网关解决方案中,路由转发过滤器扮演着至关重要的角色,负责对进站的 HTTP 请求进行精细化处理与精准调度。以下详述其核心功能及在微服务体系中的价值:
- 请求适配与重定向**** :路由转发过滤器具备强大的请求修饰能力,能够对请求的各组成部分进行灵活调整,包括但不限于请求头、主体内容、查询参数等。这种机制使得网关能够在请求抵达目标服务前对其进行定制化改造,确保其完全符合服务接口规范。此外,过滤器还支持动态重定向请求至其他目标服务,实现复杂路由场景下的精准投递。
- 安全屏障**** :作为微服务架构的入口防线,路由转发过滤器承载了关键的安全防护功能。通过集成身份验证与授权机制,过滤器能有效拦截未经授权的访问请求,确保仅授权用户方可触及特定服务资源。这一特性对于构建坚实的服务边界,防止未授权渗透,保障整个微服务生态系统安全至关重要。
- 智能缓存**** :为了提升系统性能、缓解服务压力并降低响应延迟,过滤器可集成缓存策略。针对特定请求或响应,过滤器能够识别其是否适合缓存,并在必要时直接从缓存中返回结果,避免对后端服务产生不必要的调用。这种机制在面对高并发、数据复用性强的场景时尤为高效,显著提升了系统的整体响应速度与吞吐能力。
- 日志审计与监控洞察**** :路由转发过滤器充当了微服务交互的透明观察者,实时捕获并记录请求与响应的详细信息。这些数据不仅可用于生成详细的访问日志,便于问题排查与合规审计,还能作为关键性能指标输入到监控系统,助力运维人员实时掌握服务状态,快速定位异常,确保微服务集群稳定运行。
- 流量治理与韧性保障**** :借助路由转发过滤器,网关得以实施精细的流量控制策略,如限流、熔断、降级等,以防止服务因瞬时流量激增而过载崩溃。通过智能调节进入服务的请求速率,过滤器在保障服务质量的同时,增强了系统的弹性和稳定性,为微服务架构应对各种突发情况提供了有力支撑。
- 负载均衡与服务发现**** :路由转发过滤器的核心职能之一在于实现请求到多个后端服务实例的透明转发,并依据预设的负载均衡算法,确保请求在各实例间均匀分布,最大限度利用服务资源,实现系统的水平扩展。同时,过滤器通常与服务注册与发现机制紧密集成,确保网关始终能准确找到并连接到可用的服务实例,实现服务间的无缝通信。
综上所述,Spring Cloud Gateway中的路由转发过滤器凭借其丰富的功能集与高度的可配置性,为微服务架构提供了全方位的请求处理、安全防护、性能优化、监控洞察与流量管理能力,是构建健壮、高效、易运维的微服务生态体系不可或缺的关键组件。
2、失败重试
请求重试是指在请求失败之后再次尝试请求,一般情况下重试可以减少请求因为服务GC卡顿、网络丢包、网络阻塞等短暂问题而导致的失败;然而重试会增加请求总数量,不合理的重试策略甚至可能在服务端不稳定时,导致重试流量风暴,从而压垮服务端导致故障。
请求失败一般可以按照层级划分为连接失败和请求失败;而请求一般可分为幂等和非幂等请求。
连接失败:由于TCP握手失败,实际业务请求并未发送至服务端,所以对此类错误是可以安全的重试的,配合超时配置将链接超时设置在毫秒级别,可以有效的避免偶发网络拥塞、网络丢包等网络故障导致的报错,提升整体稳定性。
请求失败:由于网络连接已经完成,实际业务请求可能已经发送至服务端,服务端的业务逻辑可能已经执行过了;比如服务端超时,而实际服务端业务逻辑会继续执行完成。因此对于幂等请求相对安全,但是对于非幂等的请求,重试可能会有较大风险。
在短视频APP例子中,比如获取账户信息的请求就是幂等请求,不会有服务端数据的修改,重试操作是比较安全的;但是对于添加评论的请求,如果请求超时进行重试,就可能导致评论服务最终收到多个添加评论的请求,最终添加多个重复的评论,显然这是不正确的,会最终导致数据异常。
因此重试配置一般可归于以下几类
- 连接重试**** : 因为连接重试风险低,收益高,一般情况下默认开启。
- 超时重试**** : 需要判断业务接口是否幂等,如非幂等风险是否可控,来决定是否启用;提供重试退避策略:重试等待固定时长或逐次提升等待时长。
- Backup Request**** : 为减少服务的延迟波动。在设置时间内未返回,再次发送请求;例如使用P99作为阈值,来降低长尾问题。
同时为了防止大规模重试导致请求量总量成倍上升,最终压垮服务,重试一般需提供熔断错误率阈值,当请求错误率超过阈值时停止重试。
3、熔断降级
服务降级是在服务所发出「实际请求需求」大于下游「稳定/可提供QPS」阈值时所使用的一种「服务维稳手段」,保障在部分极端情况下整体系统可以通过牺牲部分能力方式换来一定程度的可用性,而不是超出阈值后导致系统雪崩。
服务降级常见有两种方式,业务根据自身需求进行对应选择:
- 弃车保帅:按一定丢弃规则,仅丢弃部分请求,保障部分高优/核心 请求可以获得稳定服务。
- 贫富相均:对于所有请求一视同仁,按照相同比例丢弃。
对于基础系统/核心业务/关键服务,其组件可用性有着极高要求,如果因其承载资源需求过高而整体完全不可用,会导致大面积服务调用链直接断裂,并使故障进一步扩散,引起「系统雪崩」,其造成的巨大损失是我们不能接受的。
在短视频APP的例子中,如下图,假如因为突发事件流量,导致账户服务的流量增加触发了限流;但是对于短视频的场景下,视频播放功能价值显然高于评论功能的价值,在有限的资源情况下,账户服务如果主动将评论服务的流量进行降级,将资源腾挪给视频信息服务,舍弃评论功能,保护视频播放能力显然能获得更高性价比。
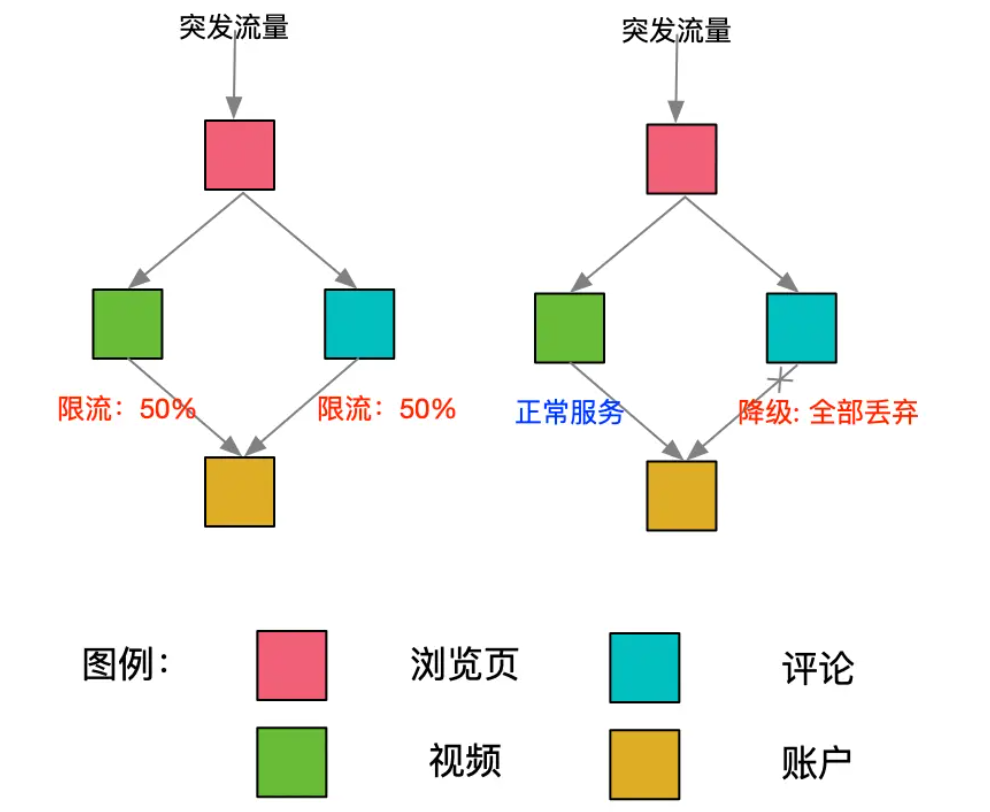
服务降级究其根本,即是“断臂求生”。对于实际业务场景而言,降级方式的评估即是对「付出成本」和「实际收获」的评估,可以从以下三个维度去抽象细化:
- 尽可能少丢弃—— “每一个请求都有价值”
- 尽可能丢弃价值较低的请求—— “请求与请求的价值是不同的”
- 尽可能丢弃性价比低的请求—— “吃了两份资源却只能产出一份价值的请求”
4、实现过程
4.1 正常路由转发
在这里创建两个服务,方便测试负载均衡和路由转发效果
这段代码和之前请求服务模块一样,将服务弄到注册中心
【自研网关系列】请求服务模块和客户端模块实现-CSDN博客
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @RestController
@ApiService(serviceId = "backend-http-server", protocol = ApiProtocol.HTTP, patternPath = "/http-server/**")
@Slf4j
public class HttpController {
@Autowired
private ApiProperties apiProperties;
@ApiInvoker(path = "/http-server/ping")
@GetMapping("/http-server/ping")
public String ping() {
log.info("{}", apiProperties);
return "pong1";
}
}
|
配置文件就是端口号和 Nacos 地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| server:
port: 8201
api:
registerAddress: 127.0.0.1:8848
env: dev
gray: false
|
启动三个类
继续 debug 来讲解流程
进入过滤器后,会根据配置中是否有熔断降级的逻辑,不是就正常路由
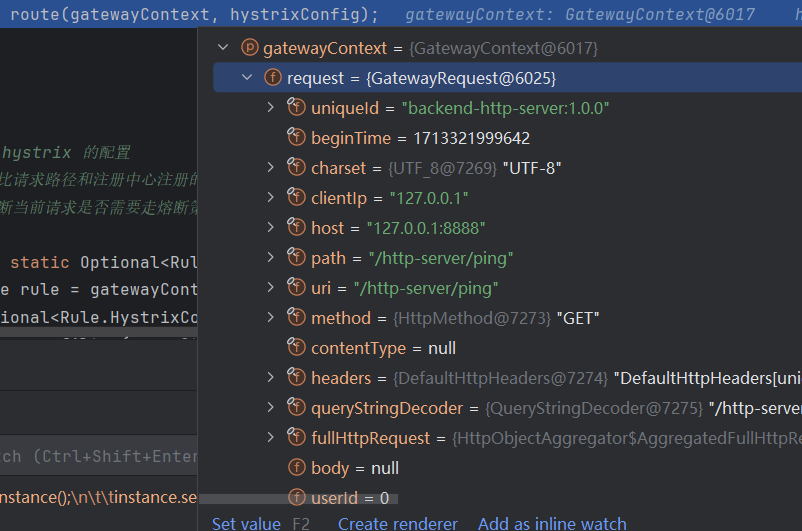
这里使用 Http 异步操作来提高性能和响应速度:
在传统的同步HTTP请求中,每个请求都需要等待服务器的响应,这会导致线程阻塞,从而降低程序的效率。而在异步HTTP请求中,请求发送后不需要等待服务器的响应,可以立即进行其他操作,当服务器响应到来时,会通过回调函数进行处理。这样可以大大提高程序的并发处理能力,从而提高程序的响应速度。
- whenComplete 方法**** :
- whenComplete**** 是一个非异步的完成方法。
- 当 CompletableFuture**** 的执行完成或者发生异常时,它提供了一个回调。
- 这个回调将在 CompletableFuture**** 执行的相同线程中执行。这意味着,如果 CompletableFuture**** 的操作是阻塞的,那么回调也会在同一个阻塞的线程中执行。
- 在这段代码中,如果 whenComplete**** 为 true**** ,则在 future**** 完成时使用 whenComplete**** 方法。这意味着 complete**** 方法将在 future**** 所在的线程中被调用。
- whenCompleteAsync 方法**** :
- whenCompleteAsync**** 是异步的完成方法。
- 它也提供了一个在 CompletableFuture**** 执行完成或者发生异常时执行的回调。
- 与 whenComplete**** 不同,这个回调将在不同的线程中异步执行。通常情况下,它将在默认的 ForkJoinPool**** 中的某个线程上执行,除非提供了自定义的 Executor**** 。
- 在代码中,如果 whenComplete**** 为 false**** ,则使用 whenCompleteAsync**** 。这意味着 complete**** 方法将在不同的线程中异步执行。
- 由于 ForkJoinPool中的线程是共用的**** ,ParallelStream中的线程也是用的ForkJoinPool,因此我推荐手动设定这个线程池的大小,否则会出现一些异常哦。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
private CompletableFuture<Response> route(GatewayContext gatewayContext, Optional<Rule.HystrixConfig> hystrixConfig) {
Request request = gatewayContext.getRequest().build();
CompletableFuture<Response> future = AsyncHttpHelper.getInstance().executeRequest(request);
boolean whenComplete = ConfigLoader.getConfig().isWhenComplete();
if (whenComplete) {
future.whenComplete(((response, throwable) -> {
complete(request, response, throwable, gatewayContext);
}));
} else {
future.whenCompleteAsync(((response, throwable) -> {
complete(request, response, throwable, gatewayContext);
}));
}
return future;
}
|
然后就是处理HTTP响应,并根据处理过程中是否存在异常来设置不同的响应内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| private void handleResponse(Request request, Response response, Throwable throwable, GatewayContext gatewayContext) {
String url = request.getUrl();
try {
if (Objects.nonNull(throwable)) {
if (throwable instanceof TimeoutException) {
log.warn("complete timeout {}", url);
gatewayContext.setThrowable(throwable);
gatewayContext.setResponse(GatewayResponse.buildGatewayResponse(ResponseCode.REQUEST_TIMEOUT));
} else if (throwable instanceof IOException) {
gatewayContext.setThrowable(new ConnectException(throwable, gatewayContext.getUniqueId(), url, ResponseCode.HTTP_RESPONSE_ERROR));
gatewayContext.setResponse(GatewayResponse.buildGatewayResponse(ResponseCode.HTTP_RESPONSE_ERROR));
}
} else {
gatewayContext.setResponse(GatewayResponse.buildGatewayResponse(response));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
gatewayContext.setThrowable(new ResponseException(ResponseCode.INTERNAL_ERROR));
gatewayContext.setResponse(GatewayResponse.buildGatewayResponse(ResponseCode.INTERNAL_ERROR));
log.error("complete process failed", e);
} finally {
gatewayContext.setContextStatus(ContextStatus.Written);
ResponseHelper.writeResponse(gatewayContext);
}
}
|
最终就是将HTTP响应写回客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public static void writeResponse(IContext context) {
context.releaseRequest();
if (context.judgeContextStatus(ContextStatus.Written)) {
FullHttpResponse response = getHttpResponse(context, (GatewayResponse) context.getResponse());
if (!context.isKeepAlive()) {
context.getNettyContext().writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
} else {
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION, HttpHeaderValues.KEEP_ALIVE);
context.getNettyContext().writeAndFlush(response);
}
context.setContextStatus(ContextStatus.Completed);
} else if (context.judgeContextStatus(ContextStatus.Completed)) {
context.invokeCompletedCallBacks();
}
}
|
这里顺便展示前面的负载均衡
这里请求的网关核心的端口,但可以访问8201或8202的端口,这就是路由转发的效果
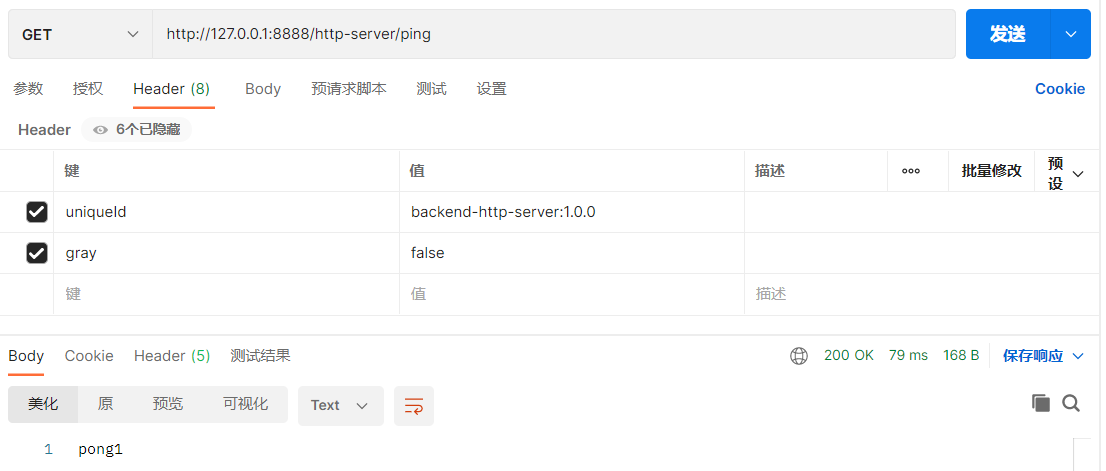
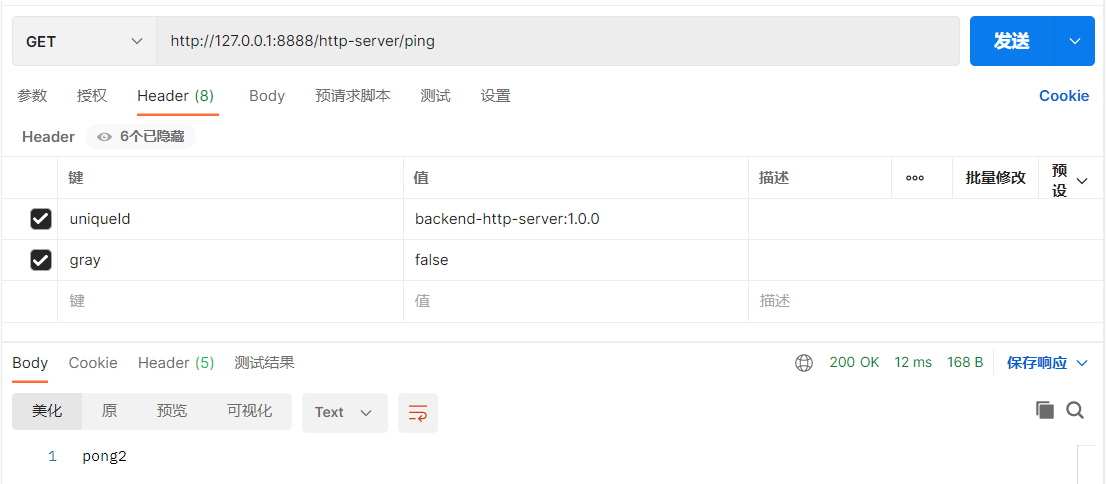
4.2 请求重试
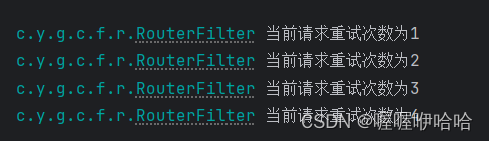
就是在处理响应请求之前就执行,然后如果有异常,且小于最大重试次数,就重新执行一遍过滤器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| private void complete(Request request, Response response, Throwable throwable, GatewayContext gatewayContext) {
gatewayContext.releaseRequest();
Rule rule = gatewayContext.getRules();
int currentRetryTimes = gatewayContext.getCurrentRetryTimes();
int confRetryTimes = rule.getRetryConfig().getTimes();
if ((throwable instanceof TimeoutException
|| throwable instanceof IOException)
&& currentRetryTimes <= confRetryTimes) {
doRetry(gatewayContext, currentRetryTimes);
}
handleResponse(request, response, throwable, gatewayContext);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private void doRetry(GatewayContext gatewayContext, int retryTimes) {
gatewayContext.setCurrentRetryTimes(retryTimes + 1);
log.info("当前请求重试次数为{}", gatewayContext.getCurrentRetryTimes());
try {
doFilter(gatewayContext);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("重试请求失败, requestId={}", gatewayContext.getUniqueId(), e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
|
4.3 熔断降级
首先在 nacos 配置中心中添加 hystrix 的配置

首先需要获得获取 hystrix 的配置
- 会判断对比请求路径和注册中心注册的路径参数
- 判断当前请求是否需要走熔断策略分支
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| private static Optional<Rule.HystrixConfig> getHystrixConfig(GatewayContext gatewayContext) {
Rule rule = gatewayContext.getRules();
Optional<Rule.HystrixConfig> hystrixConfig = rule.getHystrixConfigs().stream()
.filter(c -> StringUtils.equals(c.getPath(), gatewayContext.getRequest().getPath()))
.findFirst();
return hystrixConfig;
}
|
熔断降级请求策略
- 命令执行超过配置超时时间
- 命令执行出现异常或错误
- 连续失败率达到配置的阈值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| private void routeWithHystrix(GatewayContext gatewayContext, Optional<Rule.HystrixConfig> hystrixConfig) {
String key = gatewayContext.getUniqueId() + "." + gatewayContext.getRequest().getPath();
RouterHystrixCommand proxyCommand = null;
if (commandMap.containsKey(key)) {
proxyCommand = commandMap.get(key);
if (!hystrixConfig.get().equals(commandMap.get(key))) {
log.info("previous HystrixCommand instance hashCode: {}", proxyCommand.hashCode());
proxyCommand.updateHystrixCommandProperties(proxyCommand.getCommandKey().name());
proxyCommand = new RouterHystrixCommand(gatewayContext, hystrixConfig);
log.info("after HystrixCommand instance hashCode: {}", proxyCommand.hashCode());
commandMap.put(key, proxyCommand);
}
} else {
proxyCommand = new RouterHystrixCommand(gatewayContext, hystrixConfig);
commandMap.put(key, proxyCommand);
}
proxyCommand.execute();
}
|
其中 RouterHystrixCommand 是路由转发的内部类,RouterHystrixCommand 类的主要功能是执行实际的路由操作和熔断降级操作,它使用了 Hystrix 来实现这些功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
private class RouterHystrixCommand extends HystrixCommand<Object> {
private GatewayContext context;
private Optional<Rule.HystrixConfig> config;
public RouterHystrixCommand(GatewayContext context, Optional<Rule.HystrixConfig> config) {
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey(context.getUniqueId()))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey(context.getRequest().getPath()))
.andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults(HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter()
.withCoreSize(config.get().getCoreThreadSize()))
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults(HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
.withExecutionIsolationStrategy(HystrixCommandProperties.ExecutionIsolationStrategy.THREAD)
.withExecutionTimeoutInMilliseconds(config.get().getTimeoutInMilliseconds())
.withExecutionIsolationThreadInterruptOnTimeout(true)
.withExecutionTimeoutEnabled(true)));
this.config = config;
this.context = context;
}
@Override
protected Object run() throws Exception {
route(context, config).get();
return null;
}
@Override
protected Object getFallback() {
if (isFailedExecution() || getExecutionException() instanceof HystrixTimeoutException) {
context.setResponse(GatewayResponse.buildGatewayResponse(ResponseCode.GATEWAY_FALLBACK_TIMEOUT));
} else {
context.setResponse(GatewayResponse.buildGatewayResponse(ResponseCode.GATEWAY_FALLBACK_ERROR, config.get().getFallbackResponse()));
}
context.setContextStatus(ContextStatus.Written);
return null;
}
protected void updateHystrixCommandProperties(String commandKey) {
try {
Field field = HystrixPropertiesFactory.class.getDeclaredField("commandProperties");
field.setAccessible(true);
ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCommandProperties> commandProperties = (ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCommandProperties>) field.get(null);
log.info("before update HystrixCommandProperties: {}", commandProperties.get(commandKey));
commandProperties.remove(commandKey);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {
log.error("Remove cache in HystrixCommandFactory failed, commandKey: {}", commandKey, e);
}
}
}
|
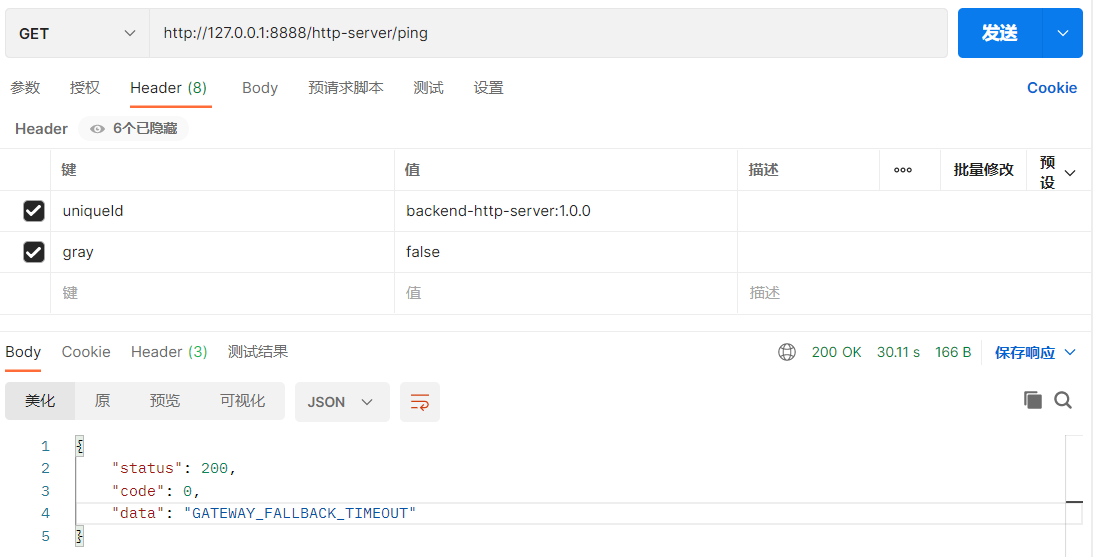
执行结果